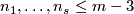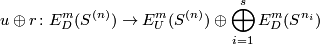High codimension links
| This page has been accepted for publication in the Bulletin of the Manifold Atlas. |
|
The user responsible for this page is Askopenkov. No other user may edit this page at present. |
Contents |
1 Introduction
Most of this page is intended not only for specialists in embeddings, but also for mathematician from other areas who want to apply or to learn the theory of embeddings.
On this page we describe the classification of embeddings 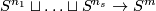 for
for 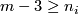 .
For the classification of embeddings in 6-space of some disconnected 3-manifolds see [Avvakumov2016], [Avvakumov2017].
.
For the classification of embeddings in 6-space of some disconnected 3-manifolds see [Avvakumov2016], [Avvakumov2017].
For a general introduction to embeddings as well as the notation and conventions used on this page, we refer to [Skopenkov2016c,  1,
1,  3].
3].
The following table was obtained by Zeeman around 1960 (see the Haefliger-Zeeman Theorem 4.1 below):
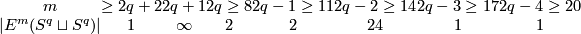
For an  -tuple
-tuple 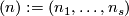 denote
denote 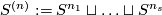 . Although
. Although 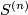 is not a manifold when
is not a manifold when 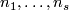 are not all equal, embeddings
are not all equal, embeddings 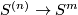 and isotopy between such embeddings are defined analogously to the case of manifolds. Denote by
and isotopy between such embeddings are defined analogously to the case of manifolds. Denote by 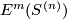 the set of embeddings
the set of embeddings 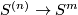 up to isotopy.
up to isotopy.
A component-wise version of embedded connected sum [Skopenkov2016c,  5] defines a commutative group structure on the set
5] defines a commutative group structure on the set 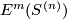 for
for 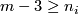 [Haefliger1966], [Haefliger1966a], [Skopenkov2015, Group Structure Lemma 2.2 and Remark 2.3.a], see [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.3].
[Haefliger1966], [Haefliger1966a], [Skopenkov2015, Group Structure Lemma 2.2 and Remark 2.3.a], see [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.3].
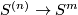 as follows. The standard embedding
as follows. The standard embedding Tex syntax erroris defined by
Tex syntax error. Fix
 pairwise disjoint
pairwise disjoint  -discs in
-discs in 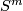 , i.e. take an embedding
, i.e. take an embedding 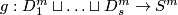 . The standard embedding
. The standard embedding 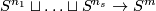 is defined as the composition
is defined as the composition Tex syntax errorof the union of the standard embeddings with
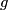 .
.
2 Examples
Recall that for any 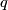 -manifold
-manifold  and
and 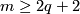 , every two embeddings
, every two embeddings 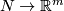 are isotopic [Skopenkov2016c, General Position Theorem 2.1], [Skopenkov2006, General Position Theorem 2.1].
The following example shows that the restriction
are isotopic [Skopenkov2016c, General Position Theorem 2.1], [Skopenkov2006, General Position Theorem 2.1].
The following example shows that the restriction 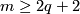 is sharp for non-connected manifolds.
is sharp for non-connected manifolds.
Example 2.1 (The Hopf Link).
For every positive integer 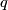 there is an embedding
there is an embedding 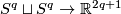 , which is not isotopic to the standard embedding.
, which is not isotopic to the standard embedding.
For 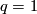 the Hopf link is shown e.g. in [Skopenkov2006, Figure 2.1.a].
For all
the Hopf link is shown e.g. in [Skopenkov2006, Figure 2.1.a].
For all 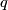 the image of the Hopf link is the union of two
the image of the Hopf link is the union of two 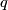 -spheres which can be described as follows:
-spheres which can be described as follows:
- either the spheres are
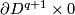 and
and 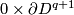 in
in 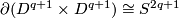 ;
;
- or they are given as the sets of points in
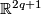 satisfying the following equations:
satisfying the following equations:
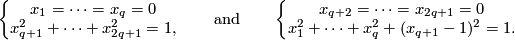
This embedding is distinguished from the standard embedding by the linking coefficient (see  3).
3).
Analogously for any 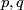 one constructs an embedding
one constructs an embedding 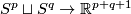 , which is not isotopic to the standard embedding. The image is the union of two spheres which can be described as follows:
, which is not isotopic to the standard embedding. The image is the union of two spheres which can be described as follows:
- either the spheres are
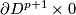 and
and 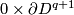 in
in 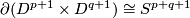 .
.
- or they are given as the points in
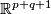 satisfying the following equations:
satisfying the following equations:
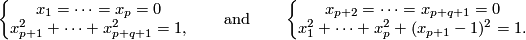
This embedding is also distinguished from the standard embedding by the linking coefficient (see  3).
3).
Definition 2.2 (The Zeeman map). We define a map
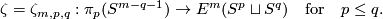
Denote by 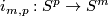 the equatorial inclusion.
For a map
the equatorial inclusion.
For a map 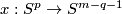 representing an element of
representing an element of 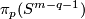 let
let
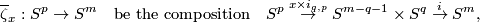
where 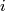 is the natural `standard embedding' defined in [Skopenkov2015a,
is the natural `standard embedding' defined in [Skopenkov2015a,  2.1], see [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.2].
We have
2.1], see [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.2].
We have 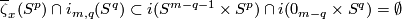 .
Let
.
Let ![\zeta[x]:=[\overline\zeta_x\sqcup i_{m,q}]](/images/math/c/4/2/c422fd90544a98b1e4657ae3f73d57f1.png) .
.
One can easily check that 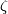 is well-defined and is a homomorphism.
is well-defined and is a homomorphism.
3 The linking coefficient
Here we define the linking coefficient and discuss is properties. Fix orientations of the standard spheres and balls.
Definition 3.1 (The linking coefficient). We define a map
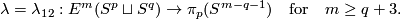
Take an embedding 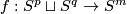 representing an element
representing an element ![[f]\in E^m(S^p\sqcup S^q)](/images/math/9/5/8/958e4adb33de7e2445e035db1cbd05a0.png) .
Take an embedding
.
Take an embedding 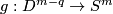 such that
such that 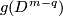 intersects
intersects 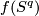 transversely at exactly one point with positive sign [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.1].
Then the restriction
transversely at exactly one point with positive sign [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.1].
Then the restriction 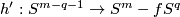 of
of 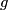 to
to 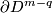 is a homotopy equivalence.
is a homotopy equivalence.
(Indeed, since 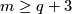 , by general position the complement
, by general position the complement 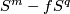 is simply-connected.
By Alexander duality,
is simply-connected.
By Alexander duality, 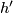 induces isomorphism in homology.
Hence by the Hurewicz and Whitehead theorems
induces isomorphism in homology.
Hence by the Hurewicz and Whitehead theorems 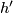 is a homotopy equivalence.)
is a homotopy equivalence.)
Let 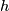 be a homotopy inverse of
be a homotopy inverse of 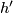 .
Define
.
Define
![\displaystyle \lambda[f]=\lambda_{12}[f]:=[S^p\xrightarrow{~f|_{S^p}~} S^m-fS^q\overset h\to S^{m-q-1}]\in\pi_p(S^{m-q-1}).](/images/math/7/0/2/702421c61c119e9f17cfea8b085f374a.png)
Remark 3.2.
(a) Clearly, ![\lambda[f]](/images/math/4/6/0/4603ad5fae840a15ed28fd021825efae.png) is well-defined, i.e. is independent of the choises of
is well-defined, i.e. is independent of the choises of 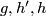 and of the representative
and of the representative 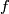 of
of ![[f]](/images/math/d/d/4/dd43b82529dd8d403c1585c5d151a163.png) .
One can check that
.
One can check that 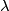 is a homomorphism.
is a homomorphism.
(b) Analogously one can define ![\lambda_{21}[f]\in\pi_q(S^{m-p-1})](/images/math/5/b/8/5b81499fd01f4267c2347d2439817f40.png) for
for 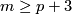 , by exchanging
, by exchanging 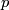 and
and 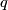 in the above definition.
in the above definition.
(c) Clearly, 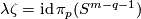 (see Definition 2.2; this also holds for
(see Definition 2.2; this also holds for 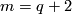 , see (d) and (e) below). So
, see (d) and (e) below). So 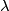 is surjective and
is surjective and 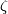 is injective.
is injective.
(d) For 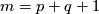 there is a simpler alternative definitions using homological ideas. That definition can be generalized to the case where the components are closed orientable manifolds. Cf. Remark 5.3.f of [Skopenkov2016e].
there is a simpler alternative definitions using homological ideas. That definition can be generalized to the case where the components are closed orientable manifolds. Cf. Remark 5.3.f of [Skopenkov2016e].
Let 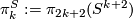 be the
be the  -th stable homotopy group of spheres.
By the Freudenthal Suspension Theorem the stable suspension homomorphism
-th stable homotopy group of spheres.
By the Freudenthal Suspension Theorem the stable suspension homomorphism 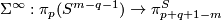 is an isomorphism for
is an isomorphism for
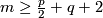 .
The stable suspension of the linking coefficient can be described as follows.
.
The stable suspension of the linking coefficient can be described as follows.
Definition 3.3 (The 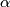 -invariant). We define a map
-invariant). We define a map
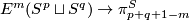 for
for 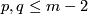 .
Take an embedding
.
Take an embedding 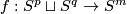 representing an element
representing an element ![[f]\in E^m(S^p\sqcup S^q)](/images/math/9/5/8/958e4adb33de7e2445e035db1cbd05a0.png) .
Define a map [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.1]
.
Define a map [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.1]
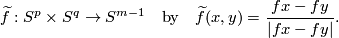
For 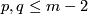 define the
define the 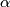 -invariant by
-invariant by
![\displaystyle \alpha[f]=[\widetilde f]\in[S^p\times S^q,S^{m-1}]\overset{v^*}\cong\pi_{p+q}(S^{m-1})\cong\pi^S_{p+q+1-m}.](/images/math/5/3/d/53debfbd4a5d88f0c6d79b4fce1d64a3.png)
The second isomorphism in this formula is the suspension isomorphism.
The map 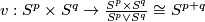 is the quotient map.
See [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.4].
The map
is the quotient map.
See [Skopenkov2006, Figure 3.4].
The map 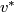 is an isomorphism for
is an isomorphism for 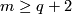 .
(For
.
(For 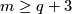 this follows by general position and for
this follows by general position and for 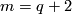 by the cofibration Barratt-Puppe exact sequence of pair
by the cofibration Barratt-Puppe exact sequence of pair 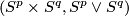 and by the existence of a retraction
and by the existence of a retraction 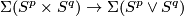 .)
.)
One can check that 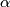 is well-defined and is a homomorphism.
is well-defined and is a homomorphism.
Lemma 3.4 [Kervaire1959a, Lemma 5.1].
We have 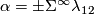 .
.
Hence 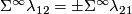 , even though in general
, even though in general 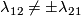 as we explain in
as we explain in  7.
7.
Note that the 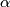 -invariant can be defined in more general situations [Koschorke1988], [Skopenkov2006,
-invariant can be defined in more general situations [Koschorke1988], [Skopenkov2006,  5].
5].
4 Classification in the metastable range
The Haefliger-Zeeman Theorem 4.1.
(D) If 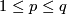 , then both
, then both 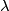 and
and 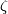 are isomorphisms for
are isomorphisms for 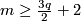 in the smooth category.
in the smooth category.
(PL) If 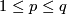 , then both
, then both 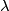 and
and 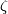 are isomorphisms for
are isomorphisms for 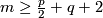 in the PL category.
in the PL category.
The surjectivity of 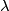 (or the injectivity of
(or the injectivity of 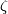 ) follows from
) follows from 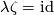 .
The injectivity of
.
The injectivity of 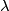 (or the surjectivity of
(or the surjectivity of 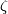 ) is proved in [Haefliger1962t], [Zeeman1962]
(or follows from [Skopenkov2006, the Haefliger-Weber Theorem 5.4 and the Deleted Product Lemma 5.3.a]).
) is proved in [Haefliger1962t], [Zeeman1962]
(or follows from [Skopenkov2006, the Haefliger-Weber Theorem 5.4 and the Deleted Product Lemma 5.3.a]).
An analogue of this result holds for links with many components, each of the same dimension [Haefliger1962t, Theorem at the end of  5], [Haefliger1966a]. Let
5], [Haefliger1966a]. Let 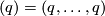 be the
be the  -tuple consisting entirely of some positive integer
-tuple consisting entirely of some positive integer 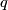 .
.
Theorem 4.2. The collection of pairwise linking coefficients
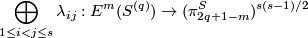
is bijective for 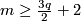 .
.
5 Examples beyond the metastable range
We present an example of the non-injectivity of the collection of pairwise linking coefficients, which shows that the dimension restriction is sharp in Theorem 4.2.
Example 5.1 (Borromean rings).
The embedding defined below is a non-trivial embedding 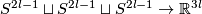 whose restrictions to each 2-component sublink is trivial [Haefliger1962, 4.1], [Haefliger1962t].
whose restrictions to each 2-component sublink is trivial [Haefliger1962, 4.1], [Haefliger1962t].
Denote coordinates in 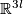 by
by 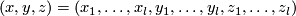 .
The (higher-dimensional) `Borromean rings' [Skopenkov2006, Figures 3.5 and 3.6] are the three spheres given by the following three systems of equations:
.
The (higher-dimensional) `Borromean rings' [Skopenkov2006, Figures 3.5 and 3.6] are the three spheres given by the following three systems of equations:
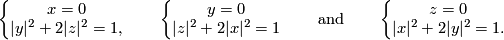
The required embedding is any embedding whose image consists of the Borromean rings.
An embedding with image the Borromean rings is distinguished from the standard embedding by the well-known triple linking number called the Massey number [Massey1968], for an elementary definition see [Skopenkov2017,  4.5 `Triple linking modulo 2' and
4.5 `Triple linking modulo 2' and  4.6 `Massey-Milnor and Sato-Levine numbers']. (Also, this embedding is not isotopic to the standard embedding because joining the three components with two tubes, i.e. `linked analogue' of embedded connected sum of the components [Skopenkov2016c], yields a non-trivial knot [Haefliger1962], cf. the Haefliger Trefoil knot [Skopenkov2016t].)
4.6 `Massey-Milnor and Sato-Levine numbers']. (Also, this embedding is not isotopic to the standard embedding because joining the three components with two tubes, i.e. `linked analogue' of embedded connected sum of the components [Skopenkov2016c], yields a non-trivial knot [Haefliger1962], cf. the Haefliger Trefoil knot [Skopenkov2016t].)
For 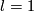 this and other results of this section are parts of low-dimensional link theory and so were known well before given references.
this and other results of this section are parts of low-dimensional link theory and so were known well before given references.
Next we present an example of the non-injectivity of the linking coefficient, which shows that the dimension restriction is sharp in Theorem 4.1.
Example 5.2 (Whitehead link). For every positive integer 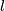 there is a non-trivial embedding
there is a non-trivial embedding 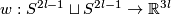 whose linking coefficient
whose linking coefficient 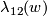 is trivial.
is trivial.
Such an embedding is obtained from the Borromean rings embedding by joining two components with a tube, i.e. by `linked analogue' of the embedded connected sum of the components [Skopenkov2016c,  3,
3,  4], cf. Wikipedia article on Whitehead link.
4], cf. Wikipedia article on Whitehead link.
We have 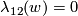 because by moving two of the three Borromean rings and self-intersecting them, we can drag the third ring apart (see details e.g. in [Skopenkov2006a]).
For
because by moving two of the three Borromean rings and self-intersecting them, we can drag the third ring apart (see details e.g. in [Skopenkov2006a]).
For 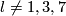 the Whitehead link is distinguished from the standard embedding by
the Whitehead link is distinguished from the standard embedding by ![\lambda_{21}(w)=[\iota_l,\iota_l]\ne0](/images/math/f/3/8/f38dc5df61caddfa7ae0c9df1fef1933.png) .
This fact should be well-known, but I do not know a published proof except [Skopenkov2015a, the Whitehead link Lemma 2.14].
For
.
This fact should be well-known, but I do not know a published proof except [Skopenkov2015a, the Whitehead link Lemma 2.14].
For 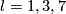 the Whitehead link is distinguished from the standard embedding by more complicated invariants [Skopenkov2006a], [Haefliger1962t,
the Whitehead link is distinguished from the standard embedding by more complicated invariants [Skopenkov2006a], [Haefliger1962t,  3].
3].
This example (in higher dimensions, i.e. for 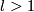 ) seems to have been discovered by Whitehead, in connection with Whitehead product.
) seems to have been discovered by Whitehead, in connection with Whitehead product.
6 Reduction to the case with unknotted components
In this section we assume that 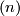 is an
is an  -tuple such that
-tuple such that 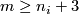 .
.
Define 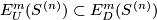 to be the subgroup of links all whose components are unknotted, i.e. isotopic to the standard embedding
to be the subgroup of links all whose components are unknotted, i.e. isotopic to the standard embedding 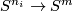 . We remark that
. We remark that 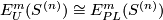 [Haefliger1966a,
[Haefliger1966a, 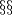 2.4, 2.6 and 9.3], [Crowley&Ferry&Skopenkov2011,
2.4, 2.6 and 9.3], [Crowley&Ferry&Skopenkov2011,  1.5].
1.5].
Define the restriction homomorphism by mapping the isotopy class of a link to the ordered  -tuple of the isotopy classes of its components:
-tuple of the isotopy classes of its components:
![\displaystyle r \colon E^m_D(S^{(n)}) \to \bigoplus_{i=1}^s E^m_D(S^{n_i}), \quad r[f]:=\oplus_{i=1}^s [f|_{S^{n_i}} \colon S^{n_i} \to S^m].](/images/math/2/5/d/25d2ec311c8371fe4ac42f34989c9ad0.png)
Take  pairwise disjoint
pairwise disjoint  -discs in
-discs in 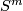 , i.e. take an embedding
, i.e. take an embedding 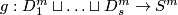 . Define
. Define
![\displaystyle j \colon \bigoplus_{i=1}^s E^m_D(S^{n_i}) \to E^m_D(S^{(n)})\quad\text{by}\quad j([f_1], \ldots, [f_s]):=[(g\circ\sqcup_{i=1}^s f_i):S^{(n)}\to S^m].](/images/math/3/2/9/329c5a3b46fae2defd6d32e45fb15014.png)
Then 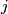 is a right inverse of the restriction homomorphism
is a right inverse of the restriction homomorphism  , i.e.
, i.e. 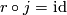 .
The unknotting homomorphism
.
The unknotting homomorphism  is defined to be the homomorphism
is defined to be the homomorphism
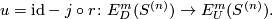
Informally, the homomorphism  is obtained by taking embedded connected sums of components with knots
is obtained by taking embedded connected sums of components with knots 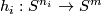 representing the elements of
representing the elements of 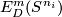 inverse to the components, whose images
inverse to the components, whose images 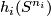 are small and are close to the components.
are small and are close to the components.
For some information on the groups 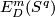 see [Skopenkov2006,
see [Skopenkov2006,  3.3]. (See also foundational paper [Haefliger1966] on
3.3]. (See also foundational paper [Haefliger1966] on 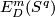 where this information is less complete and harder to find, and the foundational paper [Levine1965] on different but related group.)
where this information is less complete and harder to find, and the foundational paper [Levine1965] on different but related group.)
7 Classification beyond the metastable range
The Haefliger Theorem 7.1.
[Haefliger1966a, Theorem 10.7], [Skopenkov2009, Theorem 1.1], [Skopenkov2006b, Theorem 1.1]
If 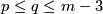 and
and 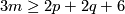 , then there is a homomorphism
, then there is a homomorphism 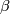 for which the following map is an isomorphism
for which the following map is an isomorphism
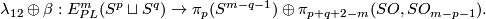
The map 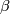 and its right inverse
and its right inverse 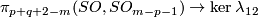 are constructed in [Haefliger1966] and [Haefliger1966a].
For alternative geometric (and presumably equivalent) definitons of
are constructed in [Haefliger1966] and [Haefliger1966a].
For alternative geometric (and presumably equivalent) definitons of 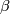 see [Skopenkov2009,
see [Skopenkov2009,  3], [Skopenkov2006b,
3], [Skopenkov2006b,  5], cf. [Skopenkov2007,
5], cf. [Skopenkov2007,  2] and [Crowley&Skopenkov2016,
2] and [Crowley&Skopenkov2016,  2.3].
2.3].
Remark 7.2.
(a) The Haefliger Theorem 7.1 implies that for any 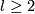 we have an isomorphism
we have an isomorphism
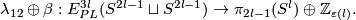
(b) For any 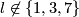 , the map
, the map
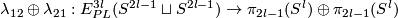
is injective and its image is 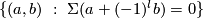 .
.
For 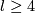 see [Haefliger1962t,
see [Haefliger1962t,  6]. The following proof for
6]. The following proof for 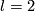 and general remark are intended for specialists.
and general remark are intended for specialists.
For 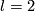 there is an exact sequence
there is an exact sequence 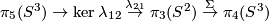 ,
where
,
where 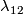 is
is 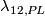 not
not 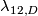 [Haefliger1966a, Corollary 10.3].
We have
[Haefliger1966a, Corollary 10.3].
We have 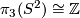 ,
, 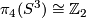 and
and 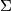 is the reduction modulo 2.
By the exactness,
is the reduction modulo 2.
By the exactness, 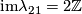 .
By (a)
.
By (a) 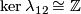 .
Hence
.
Hence  is injective.
We have
is injective.
We have 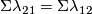 by [Haefliger1966a, Proposition 10.2].
So the formula of (b) follows.
by [Haefliger1966a, Proposition 10.2].
So the formula of (b) follows.
Analogously to [Skopenkov2009, Theorem 3.5] using geometric definitons of 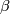 [Skopenkov2009,
[Skopenkov2009,  3], [Skopenkov2006b,
3], [Skopenkov2006b,  5] and geomeric interpretation of the EHP sequence
5] and geomeric interpretation of the EHP sequence 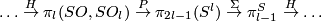 [Koschorke&Sanderson1977] one can possibly prove that
[Koschorke&Sanderson1977] one can possibly prove that 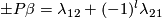 . Then (b) would follow.
. Then (b) would follow.
(c) For any 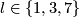 the map
the map 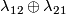 in (b) above is not injective [Haefliger1962t,
in (b) above is not injective [Haefliger1962t,  6].
6].
(d) For any 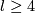 ,
, 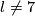 we have an isomorphism
we have an isomorphism
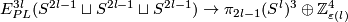
which is the sum of 3 pairwise invariants of (a) and (b) above, and the Massey number ( 7).
This follows from [Haefliger1962t,
7).
This follows from [Haefliger1962t,  6].
We conjecture that this result holds also for
6].
We conjecture that this result holds also for 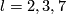 .
.
8 Classification in codimension at least 3
In this section we assume that 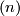 is an
is an  -tuple such that
-tuple such that 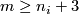 .
.
Definition 8.1 (The Haefliger link sequence). In [Haefliger1966a] Haefliger defined a long exact sequence of abelian groups
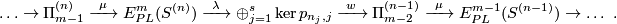
We briefly define the groups and homomorphisms in this sequence, refering to [Haefliger1966a, 1.4] for details.
In the above sequence the  -tuples
-tuples 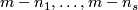 are the same for different terms.
Denote
are the same for different terms.
Denote 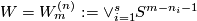 .
For any
.
For any 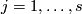 and integer
and integer 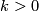 denote by
denote by 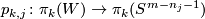 the homomorphisms induced by the projection to the
the homomorphisms induced by the projection to the 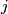 -component of the wedge.
Denote
-component of the wedge.
Denote 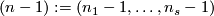 .
Denote
.
Denote 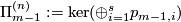 . Analogous to Definition 3.1 there is a canonical homotopy equivalence
. Analogous to Definition 3.1 there is a canonical homotopy equivalence 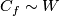 . It can be shown that each component of a link
. It can be shown that each component of a link 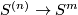 has a normal bundle with a section and so each component of a link can be pushed off along such a section into the complement.
One can show that the homotopy class of a push off of one component in the complement of the entire link gives a well-defined a map
has a normal bundle with a section and so each component of a link can be pushed off along such a section into the complement.
One can show that the homotopy class of a push off of one component in the complement of the entire link gives a well-defined a map 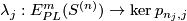 . In fact, the map
. In fact, the map 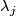 is a generalization of linking coefficient. Finally, define
is a generalization of linking coefficient. Finally, define 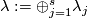 .
.
Taking the Whitehead product with the class of the identity in 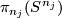 defines a homomorphism
defines a homomorphism 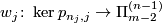 . Define
. Define 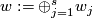 .
.
The definition of the homomorphism 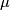 is sketched in [Haefliger1966a, 1.5].
is sketched in [Haefliger1966a, 1.5].
Theorem 8.2. (a) [Haefliger1966a, Theorem 1.3] The Haefliger link sequence is exact.
(b) [Crowley&Ferry&Skopenkov2011] The map 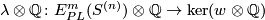 is an isomorphism.
is an isomorphism.
Part (b) follows because 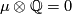 [Crowley&Ferry&Skopenkov2011, Lemma 1.3], and so the Haefliger link sequence after tensoring with the rational numbers
[Crowley&Ferry&Skopenkov2011, Lemma 1.3], and so the Haefliger link sequence after tensoring with the rational numbers 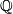 splits into short exact sequences.
splits into short exact sequences.
In [Crowley&Ferry&Skopenkov2011,  1.2,
1.2,  1.3] one can find necessary and sufficient conditions on
1.3] one can find necessary and sufficient conditions on 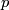 and
and 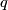 when
when 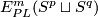 is finite, as well as an effective procedure for computing the rank of the group
is finite, as well as an effective procedure for computing the rank of the group 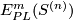 .
.
For more results related to high codimension links we refer the reader to [Skopenkov2009], [Avvakumov2016], [Avvakumov2017], [Skopenkov2015a,  2.5], [Skopenkov2016k].
2.5], [Skopenkov2016k].
9 References
- [Avvakumov2016] S. Avvakumov, The classification of certain linked 3-manifolds in 6-space, Moscow Mathematical Journal, 16:1 (2016) 1-25. http://arxiv.org/abs/1408.3918.
- [Avvakumov2017] S. Avvakumov, The classification of linked 3-manifolds in 6-space, Algebraic & Geometric Topology, to appear. arxiv preprint.
- [Crowley&Ferry&Skopenkov2011] D. Crowley, S.C. Ferry, M. Skopenkov, The rational classification of links of codimension >2, Forum Math. 26 (2014), 239-269. https://arxiv.org/abs/1106.1455
- [Crowley&Skopenkov2016] D. Crowley and A. Skopenkov, Embeddings of non-simply-connected 4-manifolds in 7-space, I. Classification modulo knots, Moscow Math. J., 21 (2021), 43--98. arXiv:1611.04738.
- [Haefliger1962] A. Haefliger, Knotted
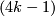 -spheres in
-spheres in 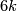 -space, Ann. of Math. (2) 75 (1962), 452–466. MR0145539 (26 #3070) Zbl 0105.17407
-space, Ann. of Math. (2) 75 (1962), 452–466. MR0145539 (26 #3070) Zbl 0105.17407
- [Haefliger1962t] A. Haefliger, Differentiable links, Topology, 1 (1962) 241--244
- [Haefliger1966] A. Haefliger, Differential embeddings of
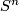 in
in 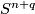 for
for 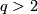 , Ann. of Math. (2) 83 (1966), 402–436. MR0202151 (34 #2024) Zbl 0151.32502
, Ann. of Math. (2) 83 (1966), 402–436. MR0202151 (34 #2024) Zbl 0151.32502
- [Haefliger1966a] A. Haefliger, Enlacements de sphères en co-dimension supérieure à 2, Comment. Math. Helv.41 (1966), 51-72. MR0212818 (35 #3683) Zbl 0149.20801
- [Kervaire1959a] M. Kervaire, An interpretation of G. Whitehead's generalization of H. Hopf's invariant, Ann. of Math. 62 (1959) 345--362.
- [Koschorke&Sanderson1977] U. Koschorke and B. Sanderson, Geometric interpretation of the generalized Hopf invariant, Math. Scand. 41 (1977) 199--217.
- [Koschorke1988] U. Koschorke, Link maps and the geometry of their invariants, Manuscripta Math. 61:4 (1988) 383--415.
- [Levine1965] J. Levine, A classification of differentiable knots, Ann. of Math. (2) 82 (1965), 15–50. MR0180981 (31 #5211) Zbl 0136.21102
- [Massey1968] W. S. Massey, Higher order linking numbers, Proc. Conf. on Algebraic Topology, Univ. Illinois, Chicago Circle, Chicago, Ill., (1968) pp. 174--205. MR0254832 (40 #8039), see also MR1625365 (99e:57016) massey.pdf.
- [Skopenkov2006] A. Skopenkov, Embedding and knotting of manifolds in Euclidean spaces, in: Surveys in Contemporary Mathematics, Ed. N. Young and Y. Choi, London Math. Soc. Lect. Notes, 347 (2008) 248-342. Available at the arXiv:0604045.
- [Skopenkov2006a] A. Skopenkov, Classification of embeddings below the metastable dimension. Available at the arXiv:0607422.
- [Skopenkov2006b] M. Skopenkov, A formula for the group of links in the 2-metastable dimension, arxiv:math/0610320v1
- [Skopenkov2007] A. Skopenkov, A new invariant and parametric connected sum of embeddings, Fund. Math. 197 (2007), 253–269. arXiv:math/0509621. MR2365891 (2008k:57044) Zbl 1145.57019
- [Skopenkov2009] M. Skopenkov, Suspension theorems for links and link maps. Proc. AMS 137 (2009) 359--369. arxiv:math/0610320, version 2 or higher
- [Skopenkov2015] M. Skopenkov, When is the set of embeddings finite up to isotopy? Intern. J. Math. 26:7 (2015), http://arxiv.org/abs/1106.1878
- [Skopenkov2015a] A. Skopenkov, A classification of knotted tori, Proc. A of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 150:2 (2020), 549-567. Full version: http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.04470
- [Skopenkov2016c] A. Skopenkov, Embeddings in Euclidean space: an introduction to their classification, to appear to Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016e] A. Skopenkov, Embeddings just below the stable range: classification, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016k] A. Skopenkov, Knotted tori, preprint.
- [Skopenkov2016t] A. Skopenkov, 3-manifolds in 6-space, to appear in Boll. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2017] A. Skopenkov, Algebraic Topology From Algorithmic Viewpoint, draft of a book.
- [Zeeman1962] E. C. Zeeman, Isotopies and knots in manifolds, Topology of 3-manifolds and related topics (Proc. The Univ. of Georgia Institute, 1961), Prentice-Hall (1962), 187–193. MR0140097 (25 #3520) Zbl 1246.57069