Talk:Thom spaces (Ex)
From Manifold Atlas
Revision as of 09:14, 2 April 2012 by Andreas Hermann (Talk | contribs)
Part 1
We define
![\displaystyle \mathrm{Th}(\xi_1)\wedge\mathrm{Th}(\xi_2)\to\mathrm{Th}(\xi_1\times\xi_2),\quad [v_1,v_2]\mapsto \left\{ \begin{array}{ll}\infty, & \textrm{if }v_1=\infty\textrm{ or }v_2=\infty \\ v_1\oplus v_2, & \textrm{else}\end{array} \right.](/images/math/3/c/e/3ce228e8d0f4c73fd415a51f186f7a96.png)
and
![\displaystyle S^1\wedge\mathrm{Th}(\xi)\to\mathrm{Th}(\xi\oplus\underline{\mathbb{R}}),\quad [z,v]\mapsto \left\{ \begin{array}{ll}\infty, & \textrm{if }z=1\textrm{ or }v=\infty \\ v\oplus\cot(\mathrm{arg}(z)/2), & \textrm{else}\end{array} \right.](/images/math/5/7/7/577cb8dd5bb5cf34994d6da143cfabe8.png)
where 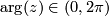 .
.
Part 2
If 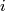 :
: 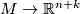 is an embedding, we denote by
is an embedding, we denote by 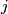 :
: 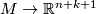 the composition
of
the composition
of 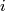 with the inclusion
with the inclusion 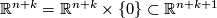 .
In particular the normal bundles are related by
.
In particular the normal bundles are related by 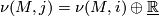 .
The bundle map
.
The bundle map 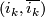 induces
induces
![\displaystyle \Omega_n(\overline{i_k}): \Omega_n(\gamma_k)\to\Omega_n(\gamma_{k+1}),\quad [M,i,f,\overline{f}]\mapsto[M,j,i_k\circ f,\overline{i_k}\circ(\overline{f}\oplus\mathrm{id}_{\underline{\mathbb{R}}})].](/images/math/a/6/9/a69fd3d13577cb882a050cf8bc388681.png)