Spivak normal fibration (Ex)
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
{{endthm}} | {{endthm}} | ||
</wikitex> | </wikitex> | ||
| − | == References == | + | <!-- == References == |
| − | {{#RefList:}} | + | {{#RefList:}} --> |
[[Category:Exercises]] | [[Category:Exercises]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Exercises without solution]] | ||
Revision as of 14:59, 1 April 2012
In the following exercises 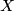 be a connected Poincaré complex of formal dimension
be a connected Poincaré complex of formal dimension  .
.
Exercise 0.1.
Let 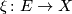 be a spherical fibration
be a spherical fibration 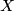 with homotopy fibre
with homotopy fibre 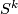 . Show that
. Show that 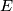 is homotopy equivalent to a Poincaré complex of formal dimension
is homotopy equivalent to a Poincaré complex of formal dimension 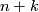 .
.
Here is an interesting problem we now confront
Problem 0.2.
Determine the Spivak normal fibration of 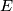 above in terms of
above in terms of 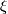 and the Spivak normal fibration of
and the Spivak normal fibration of 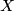 .
.
Here are some hints for this problem: Tangent bundles of bundles (Ex), [Wall1966a], [Chazin1975]
Exercise 0.3.
Let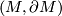 be a compact, connected, oriented,
be a compact, connected, oriented,  -dimensional manifold with boundary, embedded in
-dimensional manifold with boundary, embedded in 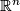 . The collapse map
. The collapse map 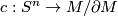 is defined by
is defined by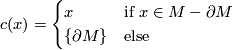
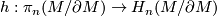 be the Hurewicz homomorphism, show that
be the Hurewicz homomorphism, show that![\displaystyle h([c])=\pm [M,\partial M]](/images/math/2/e/3/2e3fa87f344c35e33af28fa205bdcead.png)