Curvature properties of exotic spheres
(Difference between revisions)
(Created page with '<!-- COMMENT: To achieve a unified layout, along with using the template below, please OBSERVE the following: besides, $...$ and $$...$$, you should use two environments: - For…') |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<wikitex>; | <wikitex>; | ||
| − | This page is in the construction process! | + | This page is in the construction process!!! |
A homotopy sphere of dimension $n$ is an oriented closed smooth | A homotopy sphere of dimension $n$ is an oriented closed smooth | ||
| − | manifold which is homotopy equivalent to the standard sphere $S^n$. | + | manifold which is homotopy equivalent to the standard sphere $S^n$. A homotopy sphere is called an exotoc sphere if it not diffeoemeorphic to a standard sphere. |
| − | General information about homotopy spheres | + | General information about homotopy spheres (and exotoc spheres) is given on the map-page [[Exotic spheres]|Exotic spheres]. |
Revision as of 13:56, 7 June 2010
|
The user responsible for this page is Joachim. No other user may edit this page at present. |
|
This page has not been refereed. The information given here might be incomplete or provisional. |
== Introduction ==
This page is in the construction process!!!
A homotopy sphere of dimension  is an oriented closed smooth
manifold which is homotopy equivalent to the standard sphere
is an oriented closed smooth
manifold which is homotopy equivalent to the standard sphere 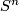 . A homotopy sphere is called an exotoc sphere if it not diffeoemeorphic to a standard sphere.
General information about homotopy spheres (and exotoc spheres) is given on the map-page [[Exotic spheres]|Exotic spheres].
. A homotopy sphere is called an exotoc sphere if it not diffeoemeorphic to a standard sphere.
General information about homotopy spheres (and exotoc spheres) is given on the map-page [[Exotic spheres]|Exotic spheres].