Isotopy
From Manifold Atlas
Two embeddings 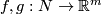 are said to be
are said to be 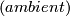 isotopic (see [Skopenkov2006], Figure 1.1), if there exists a homeomorphism onto (an ambient isotopy)
isotopic (see [Skopenkov2006], Figure 1.1), if there exists a homeomorphism onto (an ambient isotopy) 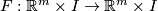 such that
such that
-
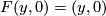 for each
for each 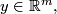
-
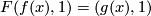 for each
for each 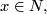 and
and
-
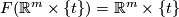 for each
for each 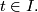
An ambient isotopy is also a homotopy 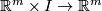 or a family of homeomorphisms
or a family of homeomorphisms 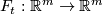 generated by the map
generated by the map 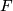 in the obvious manner.
in the obvious manner.
Evidently, isotopy is an equivalence relation on the set of embeddings of  into
into  .
.