Embeddings in Euclidean space: an introduction to their classification
| This page has been accepted for publication in the Bulletin of the Manifold Atlas. |
|
The user responsible for this page is Askopenkov. No other user may edit this page at present. |
Contents |
1 Introduction
This page is intended not only for specialists in embeddings, but also for mathematicians from other areas who want to apply or to learn the theory of embeddings. Unless otherwise indicated, the word `isotopy' means `ambient isotopy' on this page; see definition in [Skopenkov2016i].
Remark 1.1 (some motivations). The three major classical problems of topology are the following, cf. [Zeeman1993, p. 3].
- Homeomorphism Problem: Classify
 -manifolds.
-manifolds.
- Embedding Problem: Find the least dimension
 such that given space admits an embedding into
such that given space admits an embedding into  -dimensional Euclidean space
-dimensional Euclidean space  .
.
- Knotting Problem: Classify embeddings of a given space into another given space up to isotopy.
The Embedding and Knotting Problems have played an outstanding role in the development of topology. Various methods for the investigation of these problems were created by such classical figures as G. Alexander, H. Hopf, E. van Kampen, K. Kuratowski, S. MacLane, L. S. Pontryagin, R. Thom, H. Whitney, M. Atiyah, F. Hirzebruch, R. Penrose, J. H. C. Whitehead, C. Zeeman, W. Browder, J. Levine, S. P. Novikov, A. Haefliger, M. Hirsch, J. F. P. Hudson, M. Irwin and others.
The Knotting Problem is related to other branches of mathematics, most importantly, to algebraic topology (see Remark 1.4 below). See also Wikipedia article on knot theory and [Skopenkov2016t, Example 2.3].
This article gives a short guide to the problem of classifying, up to isotopy, embeddings of closed manifolds into Euclidean space or into spheres (i.e., to the Knotting Problem of Remark 1.1).
After making general remarks and giving some references we record some of the dimension ranges where no knotting is possible, i.e. where any two embeddings of  are isotopic.
We then establish notation and conventions.
We continue by introducing the connected sum operation for embeddings.
We then make some remarks on codimension 2 embeddings.
We conclude with a brief review of some important results about codimension 1 embeddings
are isotopic.
We then establish notation and conventions.
We continue by introducing the connected sum operation for embeddings.
We then make some remarks on codimension 2 embeddings.
We conclude with a brief review of some important results about codimension 1 embeddings
The most interesting and very much studied case concerns embeddings 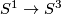 (classical knots), or more generally,
codimension 2 embeddings of spheres. Although there have been great results in the last 100 years, these results were not directly aiming at a complete classification which remains widely open. Almost nothing is said here about this, but see Wikipedia article on knot theory and
(classical knots), or more generally,
codimension 2 embeddings of spheres. Although there have been great results in the last 100 years, these results were not directly aiming at a complete classification which remains widely open. Almost nothing is said here about this, but see Wikipedia article on knot theory and  5 for more information.
5 for more information.
The Knotting Problem is known to be hard: to the best of the author's knowledge, at the time of writing there are only a few cases in which complete readily calculable classification results (see Remark 1.2) describing all isotopy classes for embeddings of a closed manifold  into Euclidean space
into Euclidean space  are known. Such classification results are the unknotting theorems in
are known. Such classification results are the unknotting theorems in  2, the results on the pages listed in Remark 1.4
and in
2, the results on the pages listed in Remark 1.4
and in  6.
Their statements, although not the proofs, are simple and accessible to non-specialists.
This page and the pages listed in Remark 1.4 concern only such classification results.
As a consequence, we leave aside a large body of work, especially but not only in codimension 2.
6.
Their statements, although not the proofs, are simple and accessible to non-specialists.
This page and the pages listed in Remark 1.4 concern only such classification results.
As a consequence, we leave aside a large body of work, especially but not only in codimension 2.
The results and remarks given below show the following:
- The complete classification of embeddings into
 of closed connected
of closed connected  -manifolds is non-trivial but presently accessible only for
-manifolds is non-trivial but presently accessible only for 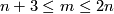 or for
or for 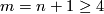 ;
;
- For a fixed
 , the more
, the more  decreases from
decreases from 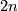 towards
towards 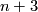 , the more complicated classification of embeddings of
, the more complicated classification of embeddings of  into
into  becomes.
becomes.
The lowest dimensional cases, i.e. all such pairs 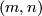 with
with 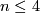 , are (6,3), (4,3), (8,4), (7,4), (5,4). For information on the cases (6,3), (8,4), (7,4) see [Skopenkov2016t], [Skopenkov2016e], [Skopenkov2016f].
, are (6,3), (4,3), (8,4), (7,4), (5,4). For information on the cases (6,3), (8,4), (7,4) see [Skopenkov2016t], [Skopenkov2016e], [Skopenkov2016f].
Remark 1.2 (Readily calculable classification). Let me informally explain what I mean by a `readily calculable classification'. (Such words are used by other people who might have a similar or a different concept.) In the best case a `readily calculable classification' is a classification in terms of (co)homology of a manifold (and certain structures on (co)homology like intersection, characteristic classes etc). A readily calculable classification is also a reduction to calculation of stable homotopy groups of spheres when these are known (or to some other standard algebraic problems involving only the homology of the manifold, which are solved in particular cases, although may be unsolved in general). An important feature of a useful classification is the accessibility of the statement to a general mathematical audience, which may only be familiar with basic notions of the area; this in turn may be viewed as an approximation to beauty. Another important feature is whether the classification gives an algorithm to classify the object considered, and if so, how fast the algorithm is.
Many readily calculable classification results are presented on this page and the
pages listed in Remark 1.4. On the other hand, in some cases `geometric problems are reduced to algebraic problems which are even harder to solve' [Wall1999], and such reductions do not give a readily calculable classification. E.g. so far an interesting approach of [Weiss96], [Goodwillie&Weiss1999] did not give any new complete readily calculable classification results. (However, it gives a modern abstract proof of certain earlier known results; it also gives explicit results on higher homotopy groups of the space of embeddings  [Weiss].)
[Weiss].)
See discusion of similar issues in [Graham&Knuth&Patashnik89, Preface].
Remark 1.3 (Embeddings into the sphere and Euclidean space).
(a) The embeddings 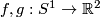 given by
given by 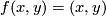 and
and 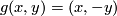 are not isotopic
(because they have distinct turning numbers; readers not familiar with turning number as defined in Wikipedia article on turning number can accept this intuitively clear assertion without proof). On the other hand, any two embeddings of
are not isotopic
(because they have distinct turning numbers; readers not familiar with turning number as defined in Wikipedia article on turning number can accept this intuitively clear assertion without proof). On the other hand, any two embeddings of 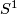 into
into 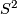 are isotopic, see Theorem 6.1.a and below.
are isotopic, see Theorem 6.1.a and below.
(b) For 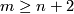 the classifications of embeddings of compact
the classifications of embeddings of compact  -manifolds into
-manifolds into 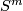 and into
and into  are the same. More precisely, for all integers
are the same. More precisely, for all integers 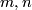 such that
such that 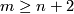 , and for every
, and for every  -manifold
-manifold  , the map
, the map 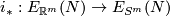 between the sets of isotopy classes of embeddings
between the sets of isotopy classes of embeddings 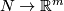 and
and 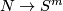 ,
which is induced by composition with the inclusion
,
which is induced by composition with the inclusion 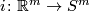 , is a bijection.
, is a bijection.
Let us prove part (b). Since 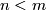 , after a small isotopy an embedding
, after a small isotopy an embedding 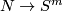 missed the point at infinity and so lies in
missed the point at infinity and so lies in 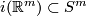 .
Hence
.
Hence 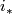 is onto.
To prove that
is onto.
To prove that 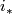 is injective, it suffices to show that if the compositions with the inclusion
is injective, it suffices to show that if the compositions with the inclusion 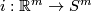 of two embeddings
of two embeddings 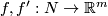 of a compact
of a compact  -manifold
-manifold  are isotopic, then
are isotopic, then 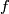 and
and 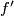 are isotopic. For showing that assume that
are isotopic. For showing that assume that 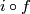 and
and 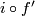 are isotopic. Then by general position
are isotopic. Then by general position 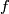 and
and 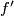 are non-ambiently isotopic. Since every non-ambient isotopy extends to an isotopy [Skopenkov2016i, Theorem 1.3],
are non-ambiently isotopic. Since every non-ambient isotopy extends to an isotopy [Skopenkov2016i, Theorem 1.3], 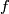 and
and 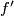 are isotopic.
are isotopic.
Remark 1.4 (References to information on the classification of embeddings). The first list is structured by the dimension of the source manifold and the target Euclidean space:
Information structured by the `complexity' of the source manifold:
For more information see e.g. [Skopenkov2006].
2 Unknotting theorems
If the category is omitted, then a result stated below holds in both the smooth and piecewise-linear (PL) category.
General Position Theorem 2.1 ([Hirsch1976, Theorem 3.5], [Rourke&Sanderson1972, Theorem 5.4]).
For every compact  -manifold
-manifold  and
and 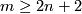 , any two embeddings of
, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
The case 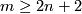 is called a `stable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there is analogous result with
is called a `stable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there is analogous result with 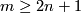 [Skopenkov2006,
[Skopenkov2006,  2]).
2]).
The restriction 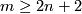 in Theorem 2.1 is sharp for non-connected manifolds, as the Hopf linking
in Theorem 2.1 is sharp for non-connected manifolds, as the Hopf linking 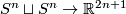 shows [Skopenkov2016h], [Skopenkov2006, Figure 2.1.a].
shows [Skopenkov2016h], [Skopenkov2006, Figure 2.1.a].
Whitney-Wu Unknotting Theorem 2.2.
For every compact connected  -manifold
-manifold  ,
, 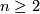 and
and 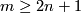 , any two embeddings of
, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
This is proved in [Wu1958], [Wu1958a] and [Wu1959] using the Whitney trick (see those rferences or [Rourke&Sanderson1972,  5]).
5]).
All the three assumptions in this result are indeed necessary:
- the assumption
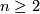 because of the existence of non-trivial knots
because of the existence of non-trivial knots 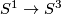 ;
;
- the connectedness assumption because of the existence of the Hopf link [Skopenkov2016h];
- the assumption
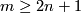 because of the example of Hudson tori [Skopenkov2016e].
because of the example of Hudson tori [Skopenkov2016e].
Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
For 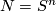 , or even for
, or even for  an integral homology
an integral homology  -sphere,
-sphere, 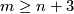 or
or 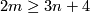 in the PL or smooth category, respectively, any two embeddings of
in the PL or smooth category, respectively, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
This result is proved in [Zeeman1960] or [Haefliger1961] in the PL or smooth category, respectively. This result is also true for 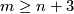 in the topological locally flat category [Stallings1963], [Gluck1963], [Rushing1973, Flattening Theorem 4.5.1], [Scharlemann1977].
in the topological locally flat category [Stallings1963], [Gluck1963], [Rushing1973, Flattening Theorem 4.5.1], [Scharlemann1977].
The case 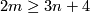 is called a `metastable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there are analogous results with
is called a `metastable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there are analogous results with 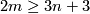 [Skopenkov2006,
[Skopenkov2006,  2,
2,  5]).
5]).
Knots in codimension 2 and the Haefliger trefoil knot [Skopenkov2016t, Example 2.1] show that the dimension restrictions are sharp (even for 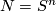 ) in the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
) in the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
Theorems 2.2 and 2.3 may be generalized as follows.
The Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4.
For every 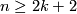 ,
, 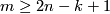 and closed
and closed  -connected
-connected  -manifold
-manifold  , any two embeddings of
, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
This was proved in [Penrose&Whitehead&Zeeman1961], [Haefliger1961], [Zeeman1962], [Irwin1965], [Hudson1969]. The proofs in [Haefliger&Hirsch1963], [Vrabec1977], [Weber1967], [Adachi1993,  7] work for homologically
7] work for homologically  -connected manifolds (see
-connected manifolds (see  3 for the definition; the proofs are non-trivial but the generalization is trivial, basically because the
3 for the definition; the proofs are non-trivial but the generalization is trivial, basically because the  -connectedness was used to ensure high enough connectedness of the complement in
-connectedness was used to ensure high enough connectedness of the complement in  to the image of
to the image of  , by Alexander duality and simple connectedness of the complement, so homological
, by Alexander duality and simple connectedness of the complement, so homological  -connectedness is sufficient).
-connectedness is sufficient).
Given Theorem 2.4 above, the case 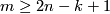 can be called a `stable range for
can be called a `stable range for  -connected manifolds'.
-connected manifolds'.
Note that if 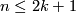 , then every closed
, then every closed  -connected
-connected  -manifold is a sphere, so the analogue of the Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4 in the smooth category is wrong, and in the PL category gives nothing more than the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
-manifold is a sphere, so the analogue of the Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4 in the smooth category is wrong, and in the PL category gives nothing more than the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
For generalizations of the Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4 see [Skopenkov2016e,  5] or [Hudson1967], [Hacon1968], [Hudson1972], [Gordon1972], [Kearton1979]. See also Theorem 6.1.
5] or [Hudson1967], [Hacon1968], [Hudson1972], [Gordon1972], [Kearton1979]. See also Theorem 6.1.
3 Notation and conventions
The following notations and conventions will be used below in this page and also in some other pages about embeddings, including those listed in Remark 1.4.
For a manifold  let
let 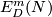 or
or 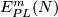 denote the set of
smooth or piecewise-linear (PL) embeddings
denote the set of
smooth or piecewise-linear (PL) embeddings 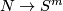 up to smooth or PL isotopy.
If the category is omitted, then the result holds (or a definition or a construction is given) in both categories.
up to smooth or PL isotopy.
If the category is omitted, then the result holds (or a definition or a construction is given) in both categories.
The sources of all embeddings are assumed to be compact.
Let 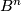 be a closed
be a closed  -ball in a closed connected
-ball in a closed connected  -manifold
-manifold  . Denote
. Denote 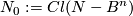 .
.
Let 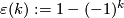 be
be  for
for  even and
even and 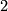 for
for  odd, so that
odd, so that 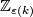 is
is 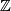 for
for  even and
even and 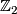 for
for  odd.
odd.
Denote by 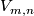 the Stiefel manifold of orthonormal
the Stiefel manifold of orthonormal  -frames in
-frames in  .
.
We omit 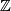 -coefficients from the notation of (co)homology groups.
-coefficients from the notation of (co)homology groups.
For a manifold 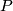 with boundary
with boundary 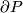 denote
denote 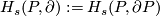 .
.
A closed manifold  is called homologically
is called homologically  -connected, if
-connected, if  is connected and
is connected and 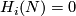 for every
for every 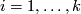 .
This condition is equivalent to
.
This condition is equivalent to 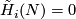 for each
for each 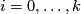 , where
, where 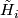 are reduced homology groups.
A pair
are reduced homology groups.
A pair 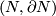 is called homologically
is called homologically  -connected, if
-connected, if 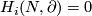 for every
for every 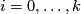 .
.
The self-intersection set of a map 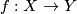 is
is 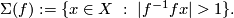
For a smooth embedding 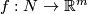 denote by
denote by
-
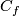 the closure of the complement in
the closure of the complement in 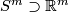 to a tight enough tubular neighborhood of
to a tight enough tubular neighborhood of 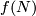 and
and
-
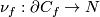 the restriction of the linear normal bundle of
the restriction of the linear normal bundle of 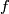 to the subspace of unit length vectors identified with
to the subspace of unit length vectors identified with 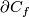 .
.
-
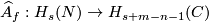 and
and 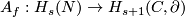 the homological Alexander duality isomorphisms, see the well-known Alexander Duality Lemmas of [Skopenkov2008], [Skopenkov2005].
the homological Alexander duality isomorphisms, see the well-known Alexander Duality Lemmas of [Skopenkov2008], [Skopenkov2005].
4 Embedded connected sum
Suppose that 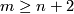 ,
,  is a closed connected
is a closed connected  -manifold and, if
-manifold and, if  is orientable, an orientation of
is orientable, an orientation of  is chosen.
Let us define the embedded connected sum operation
is chosen.
Let us define the embedded connected sum operation 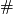 of
of 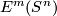 on
on 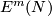 .
.
Represent isotopy classes ![[f]\in E^m(N)](/images/math/2/f/5/2f52f1701a659817e8b3dfbab85d0fef.png) and
and ![[g]\in E^m(S^n)](/images/math/0/0/3/003b3d9600f355a6b75926b59ee4b4c6.png) by embeddings
by embeddings 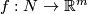 and
and 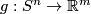 whose images are contained in disjoint balls.
Join the images of
whose images are contained in disjoint balls.
Join the images of 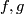 by an arc whose interior misses the images.
Let
by an arc whose interior misses the images.
Let ![[f]\#[g]](/images/math/b/5/0/b50485694938d441de43bc8d0d73e64c.png) be the isotopy class of the embedded connected sum of
be the isotopy class of the embedded connected sum of 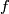 and
and 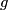 along this arc (compatible with the orientation, if
along this arc (compatible with the orientation, if  is orientable), cf. [Haefliger1966, Theorem 1.7], [Avvakumov2016,
is orientable), cf. [Haefliger1966, Theorem 1.7], [Avvakumov2016,  1].
1].
This operation is well-defined,
i.e. the isotopy class of class of the embedded connected sum depends only on the the isotopy classes ![[f]](/images/math/d/d/4/dd43b82529dd8d403c1585c5d151a163.png) and
and ![[g]](/images/math/0/8/a/08a05aeade465b1c6abe241850947aab.png) , and is independent of the choice of the path and of the representatives
, and is independent of the choice of the path and of the representatives 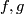 .
The proof of this fact is based on the construction of embedded connected sum of isotopies.
Although this fact is presumably classical, a proof was not written, cf. [Skopenkov2015a, Remark 2.3.a].
The proof is written for
.
The proof of this fact is based on the construction of embedded connected sum of isotopies.
Although this fact is presumably classical, a proof was not written, cf. [Skopenkov2015a, Remark 2.3.a].
The proof is written for 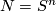 in [Skopenkov2015a,
in [Skopenkov2015a,  3, proof of the Standardization Lemma 2.1.b and beginning of proof of the Group structure Lemma 2.2 for
3, proof of the Standardization Lemma 2.1.b and beginning of proof of the Group structure Lemma 2.2 for 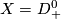 a point].
The proof for arbitrary closed connected
a point].
The proof for arbitrary closed connected  -manifold
-manifold  is analogous.
is analogous.
Moreover, for 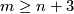 embedded connected sum defines a group structure on
embedded connected sum defines a group structure on 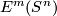 [Haefliger1966], and an action
[Haefliger1966], and an action  of
of 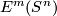 on
on 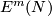 .
.
5 Some remarks on codimension 2 embeddings
The case of embeddings of 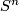 into
into 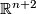 is the most extensively studied case of the Knotting Problem.
In this case there is an overwhelming multitude of isotopy classes of embeddings.
We present some speculations as to why the classification in codimension 2 should not be accessible for manifolds, not only for spheres.
is the most extensively studied case of the Knotting Problem.
In this case there is an overwhelming multitude of isotopy classes of embeddings.
We present some speculations as to why the classification in codimension 2 should not be accessible for manifolds, not only for spheres.
Let  be a closed connected
be a closed connected  -manifold.
Using embedded connected sum (
-manifold.
Using embedded connected sum ( 4) we can apparently produce an overwhelming multitude of embeddings
4) we can apparently produce an overwhelming multitude of embeddings 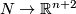 from the overwhelming multitude of embeddings
from the overwhelming multitude of embeddings 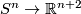 .
(However, note that for
.
(However, note that for 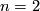 there are embeddings
there are embeddings 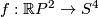 and
and 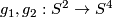 such that
such that 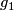 is not isotopic to
is not isotopic to 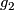 but
but 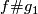 is isotopic to
is isotopic to 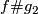 [Viro1973].)
One can also apply Artin's spinning construction [Artin1928]
[Viro1973].)
One can also apply Artin's spinning construction [Artin1928] 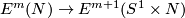 for
for 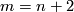 .
Thus the description of
.
Thus the description of 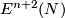 is a very hard open problem.
It would be interesting to give a more formal (e.g. algorithmic)
illustration of the hardness of this problem.
is a very hard open problem.
It would be interesting to give a more formal (e.g. algorithmic)
illustration of the hardness of this problem.
For studies of codimension 2 embeddings of manifolds up to the weaker relation of concordance see e.g. [Cappell&Shaneson1974].
6 Codimension 1 embeddings
Theorem 6.1.
(a) Any two smooth embeddings of 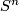 into
into 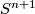 are smoothly isotopic for every
are smoothly isotopic for every 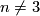 [Smale1961], [Smale1962a], [Barden1965].
[Smale1961], [Smale1962a], [Barden1965].
(b) Any two smooth embeddings of 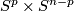 into
into 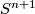 are smoothly isotopic for every
are smoothly isotopic for every 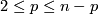 [Kosinski1961], [Wall1965], [Lucas&Neto&Saeki1996], cf. [Goldstein1967].
[Kosinski1961], [Wall1965], [Lucas&Neto&Saeki1996], cf. [Goldstein1967].
The analogue of part (a) holds
- for
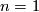 in the PL or topological category (Schöenfliess Theorem, 1912) [Rushing1973,
in the PL or topological category (Schöenfliess Theorem, 1912) [Rushing1973,  1.8].
1.8].
- for
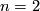 in the PL category (Alexander Theorem, 1923) [Rushing1973,
in the PL category (Alexander Theorem, 1923) [Rushing1973,  1.8].
1.8].
- for every
 in the topological locally flat category (Brown-Mazur-Moise Theorem, 1960) [Rushing1973, Generalized Schöenfliess Theorem 1.8.2].
in the topological locally flat category (Brown-Mazur-Moise Theorem, 1960) [Rushing1973, Generalized Schöenfliess Theorem 1.8.2].
The famous counterexample to the analogue of part (a) for 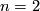 in the topological category is the Alexander horned sphere, see the corresponding Wikipedia article. The well-known very hard Schöenfliess Problem asks if each two PL embeddings of
in the topological category is the Alexander horned sphere, see the corresponding Wikipedia article. The well-known very hard Schöenfliess Problem asks if each two PL embeddings of 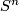 into
into 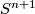 are isotopic for every
are isotopic for every 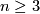 (this is equivalent to the description of
(this is equivalent to the description of 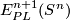 ).
).
Every embedding 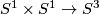 extends to an embedding either
extends to an embedding either 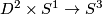 or
or 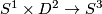 [Alexander1924]. Clearly, only the standard embedding extends to both.
[Alexander1924]. Clearly, only the standard embedding extends to both.
If it could be proven that this extension respects isotopy, this would give a 1-1 correspondence between 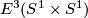 and the union of
and the union of 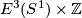 and
and 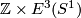 with `base points'
with `base points' 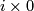 and
and 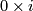 identified (where
identified (where 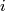 is the isotopy class of the standard inclusion
is the isotopy class of the standard inclusion 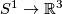 ). So the description of
). So the description of 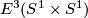 would be as hopeless as that of
would be as hopeless as that of 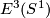 . Thus the description of
. Thus the description of 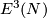 for
for  a sphere with handles is apparently hopeless.
a sphere with handles is apparently hopeless.
For more on higher-dimensional codimension 1 embeddings see e.g. [Lucas&Saeki2002].
7 References
- [Adachi1993] M. Adachi, Embeddings and immersions, Translated from the Japanese by Kiki Hudson. Translations of Mathematical Monographs, 124. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society (AMS), 1993. MR1225100 (95a:57039) Zbl 0810.57001
- [Alexander1924] J. W. Alexander, On the subdivision of 3-space by polyhedron, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 10, (1924) 6–8. Zbl 50.0659.01
- [Artin1928] E. Artin, Zur Isotopie zwei-dimensionaler Flaechen im
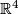 , Abh. Math. Sem. Hamburg Univ. 4 (1928) 174–177.
, Abh. Math. Sem. Hamburg Univ. 4 (1928) 174–177.
- [Avvakumov2016] S. Avvakumov, The classification of certain linked 3-manifolds in 6-space, Moscow Mathematical Journal, 16:1 (2016) 1-25. http://arxiv.org/abs/1408.3918.
- [Barden1965] D. Barden, Simply connected five-manifolds, Ann. of Math. (2) 82 (1965), 365–385. MR0184241 (32 #1714) Zbl 0136.20602
- [Cappell&Shaneson1974] S. E. Cappell and J. L. Shaneson, The codimension two placement problem and homology equivalent manifolds, Ann. of Math. (2) 99 (1974), 277–348. MR0339216 (49 #3978) Zbl 0279.57011
- [Gluck1963] H. Gluck, Unknotting
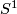 in
in 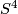 ., Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 69 (1963), 91-94. MR0142114 (25 #5507) Zbl 0108.36503
., Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 69 (1963), 91-94. MR0142114 (25 #5507) Zbl 0108.36503
- [Goldstein1967] R. Z. Goldstein, Piecewise linear unknotting of
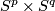 in
in 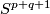 , Michigan Math. J. 14 (1967), 405–415. MR0220299 (36 #3365) Zbl 0157.54801
, Michigan Math. J. 14 (1967), 405–415. MR0220299 (36 #3365) Zbl 0157.54801
- [Goodwillie&Weiss1999] T. Goodwillie and M. Weiss, Embeddings from the point of view of immersion theory, II, Geometry and Topology, 3 (1999), 103-118. MR1694812 (2000c:57055a) Zbl 0927.57028
- [Gordon1972] C. Gordon, Embedding piecewise linear manifolds with boundary., Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 72 (1972), 21-25. MR0295359 (45 #4425) Zbl 0236.57009
- [Graham&Knuth&Patashnik89] R. Graham, D. Knuth, and O. Patashnik, Concrete Mathematics: A Foundation for Computer Science, Addison–Wesley, first published in 1989, ISBN 0-201-55802-5, https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r97002/temp/Concrete%20Mathematics%202e.pdf.
- [Hacon1968] D. Hacon, Embeddings of
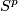 in
in 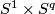 in the metastable range., Topology 7 (1968), 1-10. MR0222903 (36 #5953) Zbl 0153.53902
in the metastable range., Topology 7 (1968), 1-10. MR0222903 (36 #5953) Zbl 0153.53902
- [Haefliger&Hirsch1963] A. Haefliger and M. W. Hirsch, On the existence and classification of differentiable embeddings, Topology 2 (1963), 129–135. see also MR0149494 (26 #6981) Zbl 0113.38607
- [Haefliger1961] A. Haefliger, Plongements différentiables de variétés dans variétés., Comment. Math. Helv.36 (1961), 47-82. MR0145538 (26 #3069) Zbl 0102.38603
- [Haefliger1966] A. Haefliger, Differential embeddings of
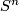 in
in 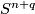 for
for 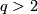 , Ann. of Math. (2) 83 (1966), 402–436. MR0202151 (34 #2024) Zbl 0151.32502
, Ann. of Math. (2) 83 (1966), 402–436. MR0202151 (34 #2024) Zbl 0151.32502
- [Hirsch1976] M. W. Hirsch, Differential topology., Graduate Texts in Mathematics, No. 33. Springer-Verlag., New York-Heidelberg, 1976. MR0448362 (56 #6669) Zbl 0356.57001
- [Hudson1967] J. Hudson, Piecewise linear embeddings, Ann. of Math. (2) 85 (1967) 1–31. MR0215308 (35 #6149) Zbl 0153.25601
- [Hudson1969] J. F. P. Hudson, Piecewise linear topology, W. A. Benjamin, Inc., New York-Amsterdam, 1969. MR0248844 (40 #2094) Zbl 0189.54507
- [Hudson1972] J. Hudson, Embeddings of bounded manifolds., Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 72 (1972), 11-20. MR0298679 (45 #7728) Zbl 0241.57006
- [Irwin1965] M. Irwin, Embeddings of polyhedral manifolds, Ann. of Math. (2) 82 (1965) 1–14. MR0182978 (32 #460) Zbl 0132.20003
- [Kearton1979] C. Kearton, Obstructions to embedding and isotopy in the metastable range, Math. Ann. 243 (1979), 103-113. MR0543720 (82k:57012) Zbl 0401.57033
- [Kosinski1961] A. Kosinski, On Alexander's theorem and knotted tori, In: Topology of 3-Manifolds, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, Ed. M.~K.~Fort, N.J., 1962, 55--57. Cf. Fort1962.
- [Lucas&Neto&Saeki1996] L. A. Lucas, O. M. Neto and O. Saeki, A generalization of Alexander's torus theorem to higher dimensions and an unknotting theorem for
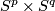 embedded in
embedded in  , Kobe J. Math. 13 (1996), no.2, 145–165. MR1442202 (98e:57041) Zbl 876.57045
, Kobe J. Math. 13 (1996), no.2, 145–165. MR1442202 (98e:57041) Zbl 876.57045
- [Lucas&Saeki2002] L. A. Lucas and O. Saeki, Embeddings of
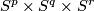 in
in 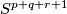 , Pacific J. Math. 207 (2002), no.2, 447–462. MR1972255 (2004c:57045) Zbl 1058.57022
, Pacific J. Math. 207 (2002), no.2, 447–462. MR1972255 (2004c:57045) Zbl 1058.57022
- [Penrose&Whitehead&Zeeman1961] R. Penrose, J. Whitehead and E. Zeeman, Imbedding of manifolds in Euclidean space., Ann. of Math. 73 (1961) 613–623. MR0124909 (23 #A2218) Zbl 0113.38101
- [Rourke&Sanderson1972] C. Rourke and B. Sanderson, Introduction to piecewise-linear topology., Ergebnisse der Mathematik und ihrer Grenzgebiete. Band 69. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer-Verlag. VIII, 1972. MR0665919 (83g:57009) Zbl 0254.57010
- [Rushing1973] T. Rushing, Topological embeddings., Pure and Applied Mathematics, 52. New York-London: Academic Press. XIII, 1973. MRMR0348752 (50 #1247) Zbl 0295.57003
- [Scharlemann1977] M. Scharlemann, Isotopy and cobordism of homology spheres in spheres., J. Lond. Math. Soc., II. Ser. 16 (1977), 559-567. MRMR0464246 (57 #4180) Zbl 0375.57003
- [Skopenkov2005] A. Skopenkov, A classification of smooth embeddings of 4-manifolds in 7-space, Topol. Appl., 157 (2010) 2094-2110. Available at the arXiv:0512594.
- [Skopenkov2006] A. Skopenkov, Embedding and knotting of manifolds in Euclidean spaces, in: Surveys in Contemporary Mathematics, Ed. N. Young and Y. Choi, London Math. Soc. Lect. Notes, 347 (2008) 248-342. Available at the arXiv:0604045.
- [Skopenkov2008] A. Skopenkov, A classification of smooth embeddings of 3-manifolds in 6-space, Math. Z. 260 (2008), no.3, 647–672. Available at the arXiv:0603429MR2434474 (2010e:57028) Zbl 1167.57013
- [Skopenkov2015a] A. Skopenkov, A classification of knotted tori, Proc. A of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 150:2 (2020), 549-567. Full version: http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.04470
- [Skopenkov2016e] A. Skopenkov, Embeddings just below the stable range: classification, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016f] A. Skopenkov, 4-manifolds in 7-space, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016h] A. Skopenkov, High codimension links, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016i] A. Skopenkov, Isotopy, submitted to Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016k] A. Skopenkov, Knotted tori, preprint.
- [Skopenkov2016t] A. Skopenkov, 3-manifolds in 6-space, to appear in Boll. Man. Atl.
- [Smale1961] S. Smale, Generalized Poincaré's conjecture in dimensions greater than four, Ann. of Math. (2) 74 (1961), 391–406. MR0137124 (25 #580) Zbl 0099.39202
- [Smale1962a] S. Smale, On the structure of manifolds, Amer. J. Math. 84 (1962), 387–399. MR0153022 (27 #2991) Zbl 0109.41103
- [Stallings1963] J. Stallings, On topologically unknotted spheres., (1963). MRMR0149458 (26 #6946) Zbl 0121.18202
- [Viro1973] O. J. Viro, Local knotting of sub-manifolds, Mat. Sb. (N.S.) 90(132) (1973), 173–183, 325. MR0370606 (51 #6833)
- [Vrabec1977] J. Vrabec, Knotting a
 -connected closed
-connected closed 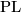
 -manifold in
-manifold in 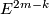 , Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 233 (1977), 137–165. MR0645405 (58 #31097) Zbl 386.57013
, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 233 (1977), 137–165. MR0645405 (58 #31097) Zbl 386.57013
- [Wall1965] C. T. C. Wall, Unknotting tori in codimension one and spheres in codimension two., Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 61 (1965), 659-664. MR0184249 (32 #1722) Zbl 0135.41602
- [Wall1999] C. T. C. Wall, Surgery on compact manifolds, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 1999. MR1687388 (2000a:57089) Zbl 0935.57003
- [Weber1967] C. Weber, Plongements de polyedres dans le domaine metastable, Comment. Math. Helv. 42 (1967), 1-27. MR0238330 (38 #6606) Zbl 0152.22402
- [Weiss] M. Weiss, private communication
- [Weiss96] M. Weiss, Calculus of Embeddings, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 33 (1996), 177-187.
- [Wu1958] W. Wu, On the realization of complexes in euclidean spaces. I, Sci. Sinica 7 (1958), 251–297. MR0099026 (20 #5471) Zbl 0183.28302
- [Wu1958a] W. Wu, On the realization of complexes in euclidean spaces. II, Sci. Sinica 7 (1958), 365–387.
- [Wu1959] W. Wu, On the realization of complexes in euclidean spaces. III, Sci. Sinica 8 (1959), 133–150. MR0098365 (20 #4825b) Zbl 0207.53104
- [Zeeman1960] E. Zeeman, Unknotting spheres in five dimensions, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 66 (1960) 198. MR0117737 (22 #8512a) Zbl 0117.40904
- [Zeeman1962] E. C. Zeeman, Isotopies and knots in manifolds, Topology of 3-manifolds and related topics (Proc. The Univ. of Georgia Institute, 1961), Prentice-Hall (1962), 187–193. MR0140097 (25 #3520) Zbl 1246.57069
- [Zeeman1993] E.C. Zeeman, A Brief History of Topology, UC Berkeley, October 27, 1993, On the occasion of Moe Hirsch's 60th birthday, http://zakuski.utsa.edu/~gokhman/ecz/hirsch60.pdf
 such that given space admits an embedding into
such that given space admits an embedding into  -dimensional Euclidean space
-dimensional Euclidean space  .
.
The Embedding and Knotting Problems have played an outstanding role in the development of topology. Various methods for the investigation of these problems were created by such classical figures as G. Alexander, H. Hopf, E. van Kampen, K. Kuratowski, S. MacLane, L. S. Pontryagin, R. Thom, H. Whitney, M. Atiyah, F. Hirzebruch, R. Penrose, J. H. C. Whitehead, C. Zeeman, W. Browder, J. Levine, S. P. Novikov, A. Haefliger, M. Hirsch, J. F. P. Hudson, M. Irwin and others.
The Knotting Problem is related to other branches of mathematics, most importantly, to algebraic topology (see Remark 1.4 below). See also Wikipedia article on knot theory and [Skopenkov2016t, Example 2.3].
This article gives a short guide to the problem of classifying, up to isotopy, embeddings of closed manifolds into Euclidean space or into spheres (i.e., to the Knotting Problem of Remark 1.1).
After making general remarks and giving some references we record some of the dimension ranges where no knotting is possible, i.e. where any two embeddings of  are isotopic.
We then establish notation and conventions.
We continue by introducing the connected sum operation for embeddings.
We then make some remarks on codimension 2 embeddings.
We conclude with a brief review of some important results about codimension 1 embeddings
are isotopic.
We then establish notation and conventions.
We continue by introducing the connected sum operation for embeddings.
We then make some remarks on codimension 2 embeddings.
We conclude with a brief review of some important results about codimension 1 embeddings
The most interesting and very much studied case concerns embeddings 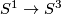 (classical knots), or more generally,
codimension 2 embeddings of spheres. Although there have been great results in the last 100 years, these results were not directly aiming at a complete classification which remains widely open. Almost nothing is said here about this, but see Wikipedia article on knot theory and
(classical knots), or more generally,
codimension 2 embeddings of spheres. Although there have been great results in the last 100 years, these results were not directly aiming at a complete classification which remains widely open. Almost nothing is said here about this, but see Wikipedia article on knot theory and  5 for more information.
5 for more information.
The Knotting Problem is known to be hard: to the best of the author's knowledge, at the time of writing there are only a few cases in which complete readily calculable classification results (see Remark 1.2) describing all isotopy classes for embeddings of a closed manifold  into Euclidean space
into Euclidean space  are known. Such classification results are the unknotting theorems in
are known. Such classification results are the unknotting theorems in  2, the results on the pages listed in Remark 1.4
and in
2, the results on the pages listed in Remark 1.4
and in  6.
Their statements, although not the proofs, are simple and accessible to non-specialists.
This page and the pages listed in Remark 1.4 concern only such classification results.
As a consequence, we leave aside a large body of work, especially but not only in codimension 2.
6.
Their statements, although not the proofs, are simple and accessible to non-specialists.
This page and the pages listed in Remark 1.4 concern only such classification results.
As a consequence, we leave aside a large body of work, especially but not only in codimension 2.
The results and remarks given below show the following:
- The complete classification of embeddings into
 of closed connected
of closed connected  -manifolds is non-trivial but presently accessible only for
-manifolds is non-trivial but presently accessible only for 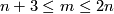 or for
or for 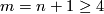 ;
;
- For a fixed
 , the more
, the more  decreases from
decreases from 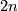 towards
towards 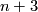 , the more complicated classification of embeddings of
, the more complicated classification of embeddings of  into
into  becomes.
becomes.
The lowest dimensional cases, i.e. all such pairs 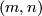 with
with 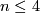 , are (6,3), (4,3), (8,4), (7,4), (5,4). For information on the cases (6,3), (8,4), (7,4) see [Skopenkov2016t], [Skopenkov2016e], [Skopenkov2016f].
, are (6,3), (4,3), (8,4), (7,4), (5,4). For information on the cases (6,3), (8,4), (7,4) see [Skopenkov2016t], [Skopenkov2016e], [Skopenkov2016f].
Remark 1.2 (Readily calculable classification). Let me informally explain what I mean by a `readily calculable classification'. (Such words are used by other people who might have a similar or a different concept.) In the best case a `readily calculable classification' is a classification in terms of (co)homology of a manifold (and certain structures on (co)homology like intersection, characteristic classes etc). A readily calculable classification is also a reduction to calculation of stable homotopy groups of spheres when these are known (or to some other standard algebraic problems involving only the homology of the manifold, which are solved in particular cases, although may be unsolved in general). An important feature of a useful classification is the accessibility of the statement to a general mathematical audience, which may only be familiar with basic notions of the area; this in turn may be viewed as an approximation to beauty. Another important feature is whether the classification gives an algorithm to classify the object considered, and if so, how fast the algorithm is.
Many readily calculable classification results are presented on this page and the
pages listed in Remark 1.4. On the other hand, in some cases `geometric problems are reduced to algebraic problems which are even harder to solve' [Wall1999], and such reductions do not give a readily calculable classification. E.g. so far an interesting approach of [Weiss96], [Goodwillie&Weiss1999] did not give any new complete readily calculable classification results. (However, it gives a modern abstract proof of certain earlier known results; it also gives explicit results on higher homotopy groups of the space of embeddings 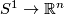 [Weiss].)
[Weiss].)
See discusion of similar issues in [Graham&Knuth&Patashnik89, Preface].
Remark 1.3 (Embeddings into the sphere and Euclidean space).
(a) The embeddings 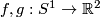 given by
given by 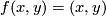 and
and 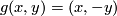 are not isotopic
(because they have distinct turning numbers; readers not familiar with turning number as defined in Wikipedia article on turning number can accept this intuitively clear assertion without proof). On the other hand, any two embeddings of
are not isotopic
(because they have distinct turning numbers; readers not familiar with turning number as defined in Wikipedia article on turning number can accept this intuitively clear assertion without proof). On the other hand, any two embeddings of 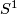 into
into 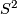 are isotopic, see Theorem 6.1.a and below.
are isotopic, see Theorem 6.1.a and below.
(b) For 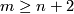 the classifications of embeddings of compact
the classifications of embeddings of compact  -manifolds into
-manifolds into 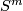 and into
and into  are the same. More precisely, for all integers
are the same. More precisely, for all integers 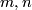 such that
such that 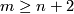 , and for every
, and for every  -manifold
-manifold  , the map
, the map 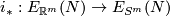 between the sets of isotopy classes of embeddings
between the sets of isotopy classes of embeddings 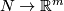 and
and 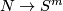 ,
which is induced by composition with the inclusion
,
which is induced by composition with the inclusion 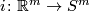 , is a bijection.
, is a bijection.
Let us prove part (b). Since 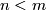 , after a small isotopy an embedding
, after a small isotopy an embedding 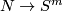 missed the point at infinity and so lies in
missed the point at infinity and so lies in 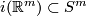 .
Hence
.
Hence 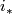 is onto.
To prove that
is onto.
To prove that 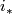 is injective, it suffices to show that if the compositions with the inclusion
is injective, it suffices to show that if the compositions with the inclusion 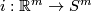 of two embeddings
of two embeddings 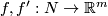 of a compact
of a compact  -manifold
-manifold  are isotopic, then
are isotopic, then 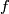 and
and 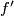 are isotopic. For showing that assume that
are isotopic. For showing that assume that 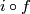 and
and 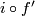 are isotopic. Then by general position
are isotopic. Then by general position 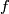 and
and 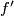 are non-ambiently isotopic. Since every non-ambient isotopy extends to an isotopy [Skopenkov2016i, Theorem 1.3],
are non-ambiently isotopic. Since every non-ambient isotopy extends to an isotopy [Skopenkov2016i, Theorem 1.3], 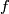 and
and 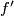 are isotopic.
are isotopic.
Remark 1.4 (References to information on the classification of embeddings). The first list is structured by the dimension of the source manifold and the target Euclidean space:
Information structured by the `complexity' of the source manifold:
For more information see e.g. [Skopenkov2006].
2 Unknotting theorems
If the category is omitted, then a result stated below holds in both the smooth and piecewise-linear (PL) category.
General Position Theorem 2.1 ([Hirsch1976, Theorem 3.5], [Rourke&Sanderson1972, Theorem 5.4]).
For every compact  -manifold
-manifold  and
and 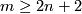 , any two embeddings of
, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
The case 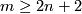 is called a `stable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there is analogous result with
is called a `stable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there is analogous result with 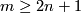 [Skopenkov2006,
[Skopenkov2006,  2]).
2]).
The restriction 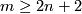 in Theorem 2.1 is sharp for non-connected manifolds, as the Hopf linking
in Theorem 2.1 is sharp for non-connected manifolds, as the Hopf linking 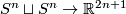 shows [Skopenkov2016h], [Skopenkov2006, Figure 2.1.a].
shows [Skopenkov2016h], [Skopenkov2006, Figure 2.1.a].
Whitney-Wu Unknotting Theorem 2.2.
For every compact connected  -manifold
-manifold  ,
, 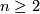 and
and 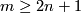 , any two embeddings of
, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
This is proved in [Wu1958], [Wu1958a] and [Wu1959] using the Whitney trick (see those rferences or [Rourke&Sanderson1972,  5]).
5]).
All the three assumptions in this result are indeed necessary:
- the assumption
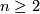 because of the existence of non-trivial knots
because of the existence of non-trivial knots 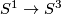 ;
;
- the connectedness assumption because of the existence of the Hopf link [Skopenkov2016h];
- the assumption
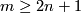 because of the example of Hudson tori [Skopenkov2016e].
because of the example of Hudson tori [Skopenkov2016e].
Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
For 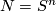 , or even for
, or even for  an integral homology
an integral homology  -sphere,
-sphere, 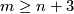 or
or 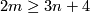 in the PL or smooth category, respectively, any two embeddings of
in the PL or smooth category, respectively, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
This result is proved in [Zeeman1960] or [Haefliger1961] in the PL or smooth category, respectively. This result is also true for 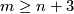 in the topological locally flat category [Stallings1963], [Gluck1963], [Rushing1973, Flattening Theorem 4.5.1], [Scharlemann1977].
in the topological locally flat category [Stallings1963], [Gluck1963], [Rushing1973, Flattening Theorem 4.5.1], [Scharlemann1977].
The case 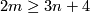 is called a `metastable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there are analogous results with
is called a `metastable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there are analogous results with 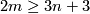 [Skopenkov2006,
[Skopenkov2006,  2,
2,  5]).
5]).
Knots in codimension 2 and the Haefliger trefoil knot [Skopenkov2016t, Example 2.1] show that the dimension restrictions are sharp (even for 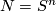 ) in the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
) in the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
Theorems 2.2 and 2.3 may be generalized as follows.
The Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4.
For every 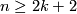 ,
, 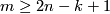 and closed
and closed  -connected
-connected  -manifold
-manifold  , any two embeddings of
, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
This was proved in [Penrose&Whitehead&Zeeman1961], [Haefliger1961], [Zeeman1962], [Irwin1965], [Hudson1969]. The proofs in [Haefliger&Hirsch1963], [Vrabec1977], [Weber1967], [Adachi1993,  7] work for homologically
7] work for homologically  -connected manifolds (see
-connected manifolds (see  3 for the definition; the proofs are non-trivial but the generalization is trivial, basically because the
3 for the definition; the proofs are non-trivial but the generalization is trivial, basically because the  -connectedness was used to ensure high enough connectedness of the complement in
-connectedness was used to ensure high enough connectedness of the complement in  to the image of
to the image of  , by Alexander duality and simple connectedness of the complement, so homological
, by Alexander duality and simple connectedness of the complement, so homological  -connectedness is sufficient).
-connectedness is sufficient).
Given Theorem 2.4 above, the case 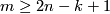 can be called a `stable range for
can be called a `stable range for  -connected manifolds'.
-connected manifolds'.
Note that if 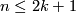 , then every closed
, then every closed  -connected
-connected  -manifold is a sphere, so the analogue of the Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4 in the smooth category is wrong, and in the PL category gives nothing more than the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
-manifold is a sphere, so the analogue of the Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4 in the smooth category is wrong, and in the PL category gives nothing more than the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
For generalizations of the Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4 see [Skopenkov2016e,  5] or [Hudson1967], [Hacon1968], [Hudson1972], [Gordon1972], [Kearton1979]. See also Theorem 6.1.
5] or [Hudson1967], [Hacon1968], [Hudson1972], [Gordon1972], [Kearton1979]. See also Theorem 6.1.
3 Notation and conventions
The following notations and conventions will be used below in this page and also in some other pages about embeddings, including those listed in Remark 1.4.
For a manifold  let
let 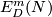 or
or 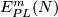 denote the set of
smooth or piecewise-linear (PL) embeddings
denote the set of
smooth or piecewise-linear (PL) embeddings 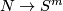 up to smooth or PL isotopy.
If the category is omitted, then the result holds (or a definition or a construction is given) in both categories.
up to smooth or PL isotopy.
If the category is omitted, then the result holds (or a definition or a construction is given) in both categories.
The sources of all embeddings are assumed to be compact.
Let 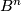 be a closed
be a closed  -ball in a closed connected
-ball in a closed connected  -manifold
-manifold  . Denote
. Denote 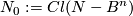 .
.
Let 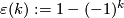 be
be  for
for  even and
even and 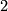 for
for  odd, so that
odd, so that 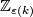 is
is 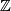 for
for  even and
even and 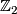 for
for  odd.
odd.
Denote by 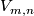 the Stiefel manifold of orthonormal
the Stiefel manifold of orthonormal  -frames in
-frames in  .
.
We omit 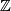 -coefficients from the notation of (co)homology groups.
-coefficients from the notation of (co)homology groups.
For a manifold 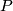 with boundary
with boundary 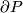 denote
denote 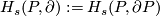 .
.
A closed manifold  is called homologically
is called homologically  -connected, if
-connected, if  is connected and
is connected and 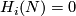 for every
for every 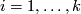 .
This condition is equivalent to
.
This condition is equivalent to 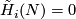 for each
for each 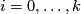 , where
, where 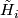 are reduced homology groups.
A pair
are reduced homology groups.
A pair 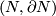 is called homologically
is called homologically  -connected, if
-connected, if 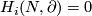 for every
for every 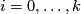 .
.
The self-intersection set of a map 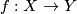 is
is 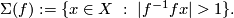
For a smooth embedding 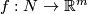 denote by
denote by
-
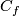 the closure of the complement in
the closure of the complement in 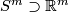 to a tight enough tubular neighborhood of
to a tight enough tubular neighborhood of 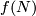 and
and
-
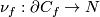 the restriction of the linear normal bundle of
the restriction of the linear normal bundle of 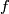 to the subspace of unit length vectors identified with
to the subspace of unit length vectors identified with 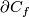 .
.
-
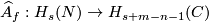 and
and 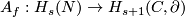 the homological Alexander duality isomorphisms, see the well-known Alexander Duality Lemmas of [Skopenkov2008], [Skopenkov2005].
the homological Alexander duality isomorphisms, see the well-known Alexander Duality Lemmas of [Skopenkov2008], [Skopenkov2005].
4 Embedded connected sum
Suppose that 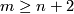 ,
,  is a closed connected
is a closed connected  -manifold and, if
-manifold and, if  is orientable, an orientation of
is orientable, an orientation of  is chosen.
Let us define the embedded connected sum operation
is chosen.
Let us define the embedded connected sum operation 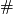 of
of 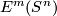 on
on 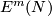 .
.
Represent isotopy classes ![[f]\in E^m(N)](/images/math/2/f/5/2f52f1701a659817e8b3dfbab85d0fef.png) and
and ![[g]\in E^m(S^n)](/images/math/0/0/3/003b3d9600f355a6b75926b59ee4b4c6.png) by embeddings
by embeddings 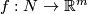 and
and 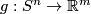 whose images are contained in disjoint balls.
Join the images of
whose images are contained in disjoint balls.
Join the images of 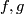 by an arc whose interior misses the images.
Let
by an arc whose interior misses the images.
Let ![[f]\#[g]](/images/math/b/5/0/b50485694938d441de43bc8d0d73e64c.png) be the isotopy class of the embedded connected sum of
be the isotopy class of the embedded connected sum of 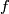 and
and 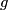 along this arc (compatible with the orientation, if
along this arc (compatible with the orientation, if  is orientable), cf. [Haefliger1966, Theorem 1.7], [Avvakumov2016,
is orientable), cf. [Haefliger1966, Theorem 1.7], [Avvakumov2016,  1].
1].
This operation is well-defined,
i.e. the isotopy class of class of the embedded connected sum depends only on the the isotopy classes ![[f]](/images/math/d/d/4/dd43b82529dd8d403c1585c5d151a163.png) and
and ![[g]](/images/math/0/8/a/08a05aeade465b1c6abe241850947aab.png) , and is independent of the choice of the path and of the representatives
, and is independent of the choice of the path and of the representatives 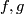 .
The proof of this fact is based on the construction of embedded connected sum of isotopies.
Although this fact is presumably classical, a proof was not written, cf. [Skopenkov2015a, Remark 2.3.a].
The proof is written for
.
The proof of this fact is based on the construction of embedded connected sum of isotopies.
Although this fact is presumably classical, a proof was not written, cf. [Skopenkov2015a, Remark 2.3.a].
The proof is written for 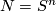 in [Skopenkov2015a,
in [Skopenkov2015a,  3, proof of the Standardization Lemma 2.1.b and beginning of proof of the Group structure Lemma 2.2 for
3, proof of the Standardization Lemma 2.1.b and beginning of proof of the Group structure Lemma 2.2 for 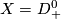 a point].
The proof for arbitrary closed connected
a point].
The proof for arbitrary closed connected  -manifold
-manifold  is analogous.
is analogous.
Moreover, for 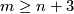 embedded connected sum defines a group structure on
embedded connected sum defines a group structure on 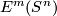 [Haefliger1966], and an action
[Haefliger1966], and an action  of
of 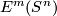 on
on 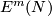 .
.
5 Some remarks on codimension 2 embeddings
The case of embeddings of 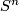 into
into 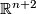 is the most extensively studied case of the Knotting Problem.
In this case there is an overwhelming multitude of isotopy classes of embeddings.
We present some speculations as to why the classification in codimension 2 should not be accessible for manifolds, not only for spheres.
is the most extensively studied case of the Knotting Problem.
In this case there is an overwhelming multitude of isotopy classes of embeddings.
We present some speculations as to why the classification in codimension 2 should not be accessible for manifolds, not only for spheres.
Let  be a closed connected
be a closed connected  -manifold.
Using embedded connected sum (
-manifold.
Using embedded connected sum ( 4) we can apparently produce an overwhelming multitude of embeddings
4) we can apparently produce an overwhelming multitude of embeddings 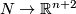 from the overwhelming multitude of embeddings
from the overwhelming multitude of embeddings 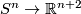 .
(However, note that for
.
(However, note that for 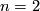 there are embeddings
there are embeddings 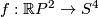 and
and 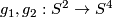 such that
such that 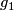 is not isotopic to
is not isotopic to 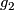 but
but 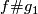 is isotopic to
is isotopic to 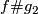 [Viro1973].)
One can also apply Artin's spinning construction [Artin1928]
[Viro1973].)
One can also apply Artin's spinning construction [Artin1928] 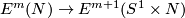 for
for 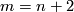 .
Thus the description of
.
Thus the description of 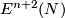 is a very hard open problem.
It would be interesting to give a more formal (e.g. algorithmic)
illustration of the hardness of this problem.
is a very hard open problem.
It would be interesting to give a more formal (e.g. algorithmic)
illustration of the hardness of this problem.
For studies of codimension 2 embeddings of manifolds up to the weaker relation of concordance see e.g. [Cappell&Shaneson1974].
6 Codimension 1 embeddings
Theorem 6.1.
(a) Any two smooth embeddings of 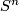 into
into 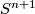 are smoothly isotopic for every
are smoothly isotopic for every 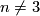 [Smale1961], [Smale1962a], [Barden1965].
[Smale1961], [Smale1962a], [Barden1965].
(b) Any two smooth embeddings of 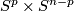 into
into 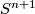 are smoothly isotopic for every
are smoothly isotopic for every 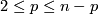 [Kosinski1961], [Wall1965], [Lucas&Neto&Saeki1996], cf. [Goldstein1967].
[Kosinski1961], [Wall1965], [Lucas&Neto&Saeki1996], cf. [Goldstein1967].
The analogue of part (a) holds
- for
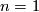 in the PL or topological category (Schöenfliess Theorem, 1912) [Rushing1973,
in the PL or topological category (Schöenfliess Theorem, 1912) [Rushing1973,  1.8].
1.8].
- for
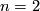 in the PL category (Alexander Theorem, 1923) [Rushing1973,
in the PL category (Alexander Theorem, 1923) [Rushing1973,  1.8].
1.8].
- for every
 in the topological locally flat category (Brown-Mazur-Moise Theorem, 1960) [Rushing1973, Generalized Schöenfliess Theorem 1.8.2].
in the topological locally flat category (Brown-Mazur-Moise Theorem, 1960) [Rushing1973, Generalized Schöenfliess Theorem 1.8.2].
The famous counterexample to the analogue of part (a) for 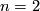 in the topological category is the Alexander horned sphere, see the corresponding Wikipedia article. The well-known very hard Schöenfliess Problem asks if each two PL embeddings of
in the topological category is the Alexander horned sphere, see the corresponding Wikipedia article. The well-known very hard Schöenfliess Problem asks if each two PL embeddings of 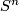 into
into 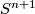 are isotopic for every
are isotopic for every 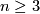 (this is equivalent to the description of
(this is equivalent to the description of 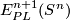 ).
).
Every embedding 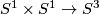 extends to an embedding either
extends to an embedding either 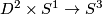 or
or 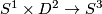 [Alexander1924]. Clearly, only the standard embedding extends to both.
[Alexander1924]. Clearly, only the standard embedding extends to both.
If it could be proven that this extension respects isotopy, this would give a 1-1 correspondence between 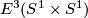 and the union of
and the union of 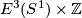 and
and 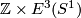 with `base points'
with `base points' 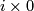 and
and 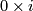 identified (where
identified (where 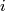 is the isotopy class of the standard inclusion
is the isotopy class of the standard inclusion 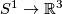 ). So the description of
). So the description of 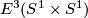 would be as hopeless as that of
would be as hopeless as that of 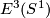 . Thus the description of
. Thus the description of 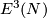 for
for  a sphere with handles is apparently hopeless.
a sphere with handles is apparently hopeless.
For more on higher-dimensional codimension 1 embeddings see e.g. [Lucas&Saeki2002].
7 References
- [Adachi1993] M. Adachi, Embeddings and immersions, Translated from the Japanese by Kiki Hudson. Translations of Mathematical Monographs, 124. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society (AMS), 1993. MR1225100 (95a:57039) Zbl 0810.57001
- [Alexander1924] J. W. Alexander, On the subdivision of 3-space by polyhedron, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 10, (1924) 6–8. Zbl 50.0659.01
- [Artin1928] E. Artin, Zur Isotopie zwei-dimensionaler Flaechen im
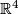 , Abh. Math. Sem. Hamburg Univ. 4 (1928) 174–177.
, Abh. Math. Sem. Hamburg Univ. 4 (1928) 174–177.
- [Avvakumov2016] S. Avvakumov, The classification of certain linked 3-manifolds in 6-space, Moscow Mathematical Journal, 16:1 (2016) 1-25. http://arxiv.org/abs/1408.3918.
- [Barden1965] D. Barden, Simply connected five-manifolds, Ann. of Math. (2) 82 (1965), 365–385. MR0184241 (32 #1714) Zbl 0136.20602
- [Cappell&Shaneson1974] S. E. Cappell and J. L. Shaneson, The codimension two placement problem and homology equivalent manifolds, Ann. of Math. (2) 99 (1974), 277–348. MR0339216 (49 #3978) Zbl 0279.57011
- [Gluck1963] H. Gluck, Unknotting
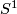 in
in 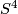 ., Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 69 (1963), 91-94. MR0142114 (25 #5507) Zbl 0108.36503
., Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 69 (1963), 91-94. MR0142114 (25 #5507) Zbl 0108.36503
- [Goldstein1967] R. Z. Goldstein, Piecewise linear unknotting of
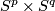 in
in 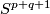 , Michigan Math. J. 14 (1967), 405–415. MR0220299 (36 #3365) Zbl 0157.54801
, Michigan Math. J. 14 (1967), 405–415. MR0220299 (36 #3365) Zbl 0157.54801
- [Goodwillie&Weiss1999] T. Goodwillie and M. Weiss, Embeddings from the point of view of immersion theory, II, Geometry and Topology, 3 (1999), 103-118. MR1694812 (2000c:57055a) Zbl 0927.57028
- [Gordon1972] C. Gordon, Embedding piecewise linear manifolds with boundary., Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 72 (1972), 21-25. MR0295359 (45 #4425) Zbl 0236.57009
- [Graham&Knuth&Patashnik89] R. Graham, D. Knuth, and O. Patashnik, Concrete Mathematics: A Foundation for Computer Science, Addison–Wesley, first published in 1989, ISBN 0-201-55802-5, https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r97002/temp/Concrete%20Mathematics%202e.pdf.
- [Hacon1968] D. Hacon, Embeddings of
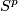 in
in 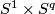 in the metastable range., Topology 7 (1968), 1-10. MR0222903 (36 #5953) Zbl 0153.53902
in the metastable range., Topology 7 (1968), 1-10. MR0222903 (36 #5953) Zbl 0153.53902
- [Haefliger&Hirsch1963] A. Haefliger and M. W. Hirsch, On the existence and classification of differentiable embeddings, Topology 2 (1963), 129–135. see also MR0149494 (26 #6981) Zbl 0113.38607
- [Haefliger1961] A. Haefliger, Plongements différentiables de variétés dans variétés., Comment. Math. Helv.36 (1961), 47-82. MR0145538 (26 #3069) Zbl 0102.38603
- [Haefliger1966] A. Haefliger, Differential embeddings of
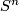 in
in 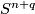 for
for 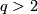 , Ann. of Math. (2) 83 (1966), 402–436. MR0202151 (34 #2024) Zbl 0151.32502
, Ann. of Math. (2) 83 (1966), 402–436. MR0202151 (34 #2024) Zbl 0151.32502
- [Hirsch1976] M. W. Hirsch, Differential topology., Graduate Texts in Mathematics, No. 33. Springer-Verlag., New York-Heidelberg, 1976. MR0448362 (56 #6669) Zbl 0356.57001
- [Hudson1967] J. Hudson, Piecewise linear embeddings, Ann. of Math. (2) 85 (1967) 1–31. MR0215308 (35 #6149) Zbl 0153.25601
- [Hudson1969] J. F. P. Hudson, Piecewise linear topology, W. A. Benjamin, Inc., New York-Amsterdam, 1969. MR0248844 (40 #2094) Zbl 0189.54507
- [Hudson1972] J. Hudson, Embeddings of bounded manifolds., Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 72 (1972), 11-20. MR0298679 (45 #7728) Zbl 0241.57006
- [Irwin1965] M. Irwin, Embeddings of polyhedral manifolds, Ann. of Math. (2) 82 (1965) 1–14. MR0182978 (32 #460) Zbl 0132.20003
- [Kearton1979] C. Kearton, Obstructions to embedding and isotopy in the metastable range, Math. Ann. 243 (1979), 103-113. MR0543720 (82k:57012) Zbl 0401.57033
- [Kosinski1961] A. Kosinski, On Alexander's theorem and knotted tori, In: Topology of 3-Manifolds, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, Ed. M.~K.~Fort, N.J., 1962, 55--57. Cf. Fort1962.
- [Lucas&Neto&Saeki1996] L. A. Lucas, O. M. Neto and O. Saeki, A generalization of Alexander's torus theorem to higher dimensions and an unknotting theorem for
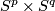 embedded in
embedded in  , Kobe J. Math. 13 (1996), no.2, 145–165. MR1442202 (98e:57041) Zbl 876.57045
, Kobe J. Math. 13 (1996), no.2, 145–165. MR1442202 (98e:57041) Zbl 876.57045
- [Lucas&Saeki2002] L. A. Lucas and O. Saeki, Embeddings of
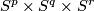 in
in 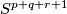 , Pacific J. Math. 207 (2002), no.2, 447–462. MR1972255 (2004c:57045) Zbl 1058.57022
, Pacific J. Math. 207 (2002), no.2, 447–462. MR1972255 (2004c:57045) Zbl 1058.57022
- [Penrose&Whitehead&Zeeman1961] R. Penrose, J. Whitehead and E. Zeeman, Imbedding of manifolds in Euclidean space., Ann. of Math. 73 (1961) 613–623. MR0124909 (23 #A2218) Zbl 0113.38101
- [Rourke&Sanderson1972] C. Rourke and B. Sanderson, Introduction to piecewise-linear topology., Ergebnisse der Mathematik und ihrer Grenzgebiete. Band 69. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer-Verlag. VIII, 1972. MR0665919 (83g:57009) Zbl 0254.57010
- [Rushing1973] T. Rushing, Topological embeddings., Pure and Applied Mathematics, 52. New York-London: Academic Press. XIII, 1973. MRMR0348752 (50 #1247) Zbl 0295.57003
- [Scharlemann1977] M. Scharlemann, Isotopy and cobordism of homology spheres in spheres., J. Lond. Math. Soc., II. Ser. 16 (1977), 559-567. MRMR0464246 (57 #4180) Zbl 0375.57003
- [Skopenkov2005] A. Skopenkov, A classification of smooth embeddings of 4-manifolds in 7-space, Topol. Appl., 157 (2010) 2094-2110. Available at the arXiv:0512594.
- [Skopenkov2006] A. Skopenkov, Embedding and knotting of manifolds in Euclidean spaces, in: Surveys in Contemporary Mathematics, Ed. N. Young and Y. Choi, London Math. Soc. Lect. Notes, 347 (2008) 248-342. Available at the arXiv:0604045.
- [Skopenkov2008] A. Skopenkov, A classification of smooth embeddings of 3-manifolds in 6-space, Math. Z. 260 (2008), no.3, 647–672. Available at the arXiv:0603429MR2434474 (2010e:57028) Zbl 1167.57013
- [Skopenkov2015a] A. Skopenkov, A classification of knotted tori, Proc. A of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 150:2 (2020), 549-567. Full version: http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.04470
- [Skopenkov2016e] A. Skopenkov, Embeddings just below the stable range: classification, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016f] A. Skopenkov, 4-manifolds in 7-space, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016h] A. Skopenkov, High codimension links, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016i] A. Skopenkov, Isotopy, submitted to Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016k] A. Skopenkov, Knotted tori, preprint.
- [Skopenkov2016t] A. Skopenkov, 3-manifolds in 6-space, to appear in Boll. Man. Atl.
- [Smale1961] S. Smale, Generalized Poincaré's conjecture in dimensions greater than four, Ann. of Math. (2) 74 (1961), 391–406. MR0137124 (25 #580) Zbl 0099.39202
- [Smale1962a] S. Smale, On the structure of manifolds, Amer. J. Math. 84 (1962), 387–399. MR0153022 (27 #2991) Zbl 0109.41103
- [Stallings1963] J. Stallings, On topologically unknotted spheres., (1963). MRMR0149458 (26 #6946) Zbl 0121.18202
- [Viro1973] O. J. Viro, Local knotting of sub-manifolds, Mat. Sb. (N.S.) 90(132) (1973), 173–183, 325. MR0370606 (51 #6833)
- [Vrabec1977] J. Vrabec, Knotting a
 -connected closed
-connected closed 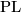
 -manifold in
-manifold in 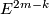 , Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 233 (1977), 137–165. MR0645405 (58 #31097) Zbl 386.57013
, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 233 (1977), 137–165. MR0645405 (58 #31097) Zbl 386.57013
- [Wall1965] C. T. C. Wall, Unknotting tori in codimension one and spheres in codimension two., Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 61 (1965), 659-664. MR0184249 (32 #1722) Zbl 0135.41602
- [Wall1999] C. T. C. Wall, Surgery on compact manifolds, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 1999. MR1687388 (2000a:57089) Zbl 0935.57003
- [Weber1967] C. Weber, Plongements de polyedres dans le domaine metastable, Comment. Math. Helv. 42 (1967), 1-27. MR0238330 (38 #6606) Zbl 0152.22402
- [Weiss] M. Weiss, private communication
- [Weiss96] M. Weiss, Calculus of Embeddings, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 33 (1996), 177-187.
- [Wu1958] W. Wu, On the realization of complexes in euclidean spaces. I, Sci. Sinica 7 (1958), 251–297. MR0099026 (20 #5471) Zbl 0183.28302
- [Wu1958a] W. Wu, On the realization of complexes in euclidean spaces. II, Sci. Sinica 7 (1958), 365–387.
- [Wu1959] W. Wu, On the realization of complexes in euclidean spaces. III, Sci. Sinica 8 (1959), 133–150. MR0098365 (20 #4825b) Zbl 0207.53104
- [Zeeman1960] E. Zeeman, Unknotting spheres in five dimensions, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 66 (1960) 198. MR0117737 (22 #8512a) Zbl 0117.40904
- [Zeeman1962] E. C. Zeeman, Isotopies and knots in manifolds, Topology of 3-manifolds and related topics (Proc. The Univ. of Georgia Institute, 1961), Prentice-Hall (1962), 187–193. MR0140097 (25 #3520) Zbl 1246.57069
- [Zeeman1993] E.C. Zeeman, A Brief History of Topology, UC Berkeley, October 27, 1993, On the occasion of Moe Hirsch's 60th birthday, http://zakuski.utsa.edu/~gokhman/ecz/hirsch60.pdf
 such that given space admits an embedding into
such that given space admits an embedding into  -dimensional Euclidean space
-dimensional Euclidean space  .
.
The Embedding and Knotting Problems have played an outstanding role in the development of topology. Various methods for the investigation of these problems were created by such classical figures as G. Alexander, H. Hopf, E. van Kampen, K. Kuratowski, S. MacLane, L. S. Pontryagin, R. Thom, H. Whitney, M. Atiyah, F. Hirzebruch, R. Penrose, J. H. C. Whitehead, C. Zeeman, W. Browder, J. Levine, S. P. Novikov, A. Haefliger, M. Hirsch, J. F. P. Hudson, M. Irwin and others.
The Knotting Problem is related to other branches of mathematics, most importantly, to algebraic topology (see Remark 1.4 below). See also Wikipedia article on knot theory and [Skopenkov2016t, Example 2.3].
This article gives a short guide to the problem of classifying, up to isotopy, embeddings of closed manifolds into Euclidean space or into spheres (i.e., to the Knotting Problem of Remark 1.1).
After making general remarks and giving some references we record some of the dimension ranges where no knotting is possible, i.e. where any two embeddings of  are isotopic.
We then establish notation and conventions.
We continue by introducing the connected sum operation for embeddings.
We then make some remarks on codimension 2 embeddings.
We conclude with a brief review of some important results about codimension 1 embeddings
are isotopic.
We then establish notation and conventions.
We continue by introducing the connected sum operation for embeddings.
We then make some remarks on codimension 2 embeddings.
We conclude with a brief review of some important results about codimension 1 embeddings
The most interesting and very much studied case concerns embeddings 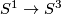 (classical knots), or more generally,
codimension 2 embeddings of spheres. Although there have been great results in the last 100 years, these results were not directly aiming at a complete classification which remains widely open. Almost nothing is said here about this, but see Wikipedia article on knot theory and
(classical knots), or more generally,
codimension 2 embeddings of spheres. Although there have been great results in the last 100 years, these results were not directly aiming at a complete classification which remains widely open. Almost nothing is said here about this, but see Wikipedia article on knot theory and  5 for more information.
5 for more information.
The Knotting Problem is known to be hard: to the best of the author's knowledge, at the time of writing there are only a few cases in which complete readily calculable classification results (see Remark 1.2) describing all isotopy classes for embeddings of a closed manifold  into Euclidean space
into Euclidean space  are known. Such classification results are the unknotting theorems in
are known. Such classification results are the unknotting theorems in  2, the results on the pages listed in Remark 1.4
and in
2, the results on the pages listed in Remark 1.4
and in  6.
Their statements, although not the proofs, are simple and accessible to non-specialists.
This page and the pages listed in Remark 1.4 concern only such classification results.
As a consequence, we leave aside a large body of work, especially but not only in codimension 2.
6.
Their statements, although not the proofs, are simple and accessible to non-specialists.
This page and the pages listed in Remark 1.4 concern only such classification results.
As a consequence, we leave aside a large body of work, especially but not only in codimension 2.
The results and remarks given below show the following:
- The complete classification of embeddings into
 of closed connected
of closed connected  -manifolds is non-trivial but presently accessible only for
-manifolds is non-trivial but presently accessible only for 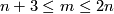 or for
or for 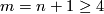 ;
;
- For a fixed
 , the more
, the more  decreases from
decreases from 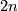 towards
towards 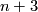 , the more complicated classification of embeddings of
, the more complicated classification of embeddings of  into
into  becomes.
becomes.
The lowest dimensional cases, i.e. all such pairs 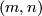 with
with 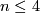 , are (6,3), (4,3), (8,4), (7,4), (5,4). For information on the cases (6,3), (8,4), (7,4) see [Skopenkov2016t], [Skopenkov2016e], [Skopenkov2016f].
, are (6,3), (4,3), (8,4), (7,4), (5,4). For information on the cases (6,3), (8,4), (7,4) see [Skopenkov2016t], [Skopenkov2016e], [Skopenkov2016f].
Remark 1.2 (Readily calculable classification). Let me informally explain what I mean by a `readily calculable classification'. (Such words are used by other people who might have a similar or a different concept.) In the best case a `readily calculable classification' is a classification in terms of (co)homology of a manifold (and certain structures on (co)homology like intersection, characteristic classes etc). A readily calculable classification is also a reduction to calculation of stable homotopy groups of spheres when these are known (or to some other standard algebraic problems involving only the homology of the manifold, which are solved in particular cases, although may be unsolved in general). An important feature of a useful classification is the accessibility of the statement to a general mathematical audience, which may only be familiar with basic notions of the area; this in turn may be viewed as an approximation to beauty. Another important feature is whether the classification gives an algorithm to classify the object considered, and if so, how fast the algorithm is.
Many readily calculable classification results are presented on this page and the
pages listed in Remark 1.4. On the other hand, in some cases `geometric problems are reduced to algebraic problems which are even harder to solve' [Wall1999], and such reductions do not give a readily calculable classification. E.g. so far an interesting approach of [Weiss96], [Goodwillie&Weiss1999] did not give any new complete readily calculable classification results. (However, it gives a modern abstract proof of certain earlier known results; it also gives explicit results on higher homotopy groups of the space of embeddings 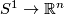 [Weiss].)
[Weiss].)
See discusion of similar issues in [Graham&Knuth&Patashnik89, Preface].
Remark 1.3 (Embeddings into the sphere and Euclidean space).
(a) The embeddings 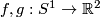 given by
given by 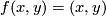 and
and 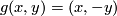 are not isotopic
(because they have distinct turning numbers; readers not familiar with turning number as defined in Wikipedia article on turning number can accept this intuitively clear assertion without proof). On the other hand, any two embeddings of
are not isotopic
(because they have distinct turning numbers; readers not familiar with turning number as defined in Wikipedia article on turning number can accept this intuitively clear assertion without proof). On the other hand, any two embeddings of 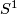 into
into 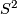 are isotopic, see Theorem 6.1.a and below.
are isotopic, see Theorem 6.1.a and below.
(b) For 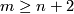 the classifications of embeddings of compact
the classifications of embeddings of compact  -manifolds into
-manifolds into 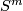 and into
and into  are the same. More precisely, for all integers
are the same. More precisely, for all integers 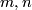 such that
such that 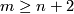 , and for every
, and for every  -manifold
-manifold  , the map
, the map 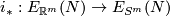 between the sets of isotopy classes of embeddings
between the sets of isotopy classes of embeddings 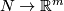 and
and 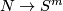 ,
which is induced by composition with the inclusion
,
which is induced by composition with the inclusion 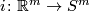 , is a bijection.
, is a bijection.
Let us prove part (b). Since 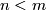 , after a small isotopy an embedding
, after a small isotopy an embedding 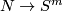 missed the point at infinity and so lies in
missed the point at infinity and so lies in 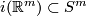 .
Hence
.
Hence 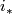 is onto.
To prove that
is onto.
To prove that 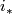 is injective, it suffices to show that if the compositions with the inclusion
is injective, it suffices to show that if the compositions with the inclusion 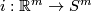 of two embeddings
of two embeddings 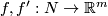 of a compact
of a compact  -manifold
-manifold  are isotopic, then
are isotopic, then 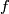 and
and 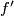 are isotopic. For showing that assume that
are isotopic. For showing that assume that 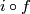 and
and 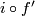 are isotopic. Then by general position
are isotopic. Then by general position 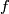 and
and 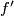 are non-ambiently isotopic. Since every non-ambient isotopy extends to an isotopy [Skopenkov2016i, Theorem 1.3],
are non-ambiently isotopic. Since every non-ambient isotopy extends to an isotopy [Skopenkov2016i, Theorem 1.3], 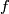 and
and 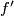 are isotopic.
are isotopic.
Remark 1.4 (References to information on the classification of embeddings). The first list is structured by the dimension of the source manifold and the target Euclidean space:
Information structured by the `complexity' of the source manifold:
For more information see e.g. [Skopenkov2006].
2 Unknotting theorems
If the category is omitted, then a result stated below holds in both the smooth and piecewise-linear (PL) category.
General Position Theorem 2.1 ([Hirsch1976, Theorem 3.5], [Rourke&Sanderson1972, Theorem 5.4]).
For every compact  -manifold
-manifold  and
and 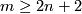 , any two embeddings of
, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
The case 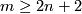 is called a `stable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there is analogous result with
is called a `stable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there is analogous result with 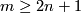 [Skopenkov2006,
[Skopenkov2006,  2]).
2]).
The restriction 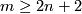 in Theorem 2.1 is sharp for non-connected manifolds, as the Hopf linking
in Theorem 2.1 is sharp for non-connected manifolds, as the Hopf linking 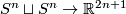 shows [Skopenkov2016h], [Skopenkov2006, Figure 2.1.a].
shows [Skopenkov2016h], [Skopenkov2006, Figure 2.1.a].
Whitney-Wu Unknotting Theorem 2.2.
For every compact connected  -manifold
-manifold  ,
, 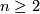 and
and 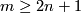 , any two embeddings of
, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
This is proved in [Wu1958], [Wu1958a] and [Wu1959] using the Whitney trick (see those rferences or [Rourke&Sanderson1972,  5]).
5]).
All the three assumptions in this result are indeed necessary:
- the assumption
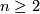 because of the existence of non-trivial knots
because of the existence of non-trivial knots 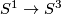 ;
;
- the connectedness assumption because of the existence of the Hopf link [Skopenkov2016h];
- the assumption
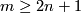 because of the example of Hudson tori [Skopenkov2016e].
because of the example of Hudson tori [Skopenkov2016e].
Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
For 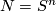 , or even for
, or even for  an integral homology
an integral homology  -sphere,
-sphere, 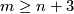 or
or 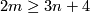 in the PL or smooth category, respectively, any two embeddings of
in the PL or smooth category, respectively, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
This result is proved in [Zeeman1960] or [Haefliger1961] in the PL or smooth category, respectively. This result is also true for 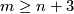 in the topological locally flat category [Stallings1963], [Gluck1963], [Rushing1973, Flattening Theorem 4.5.1], [Scharlemann1977].
in the topological locally flat category [Stallings1963], [Gluck1963], [Rushing1973, Flattening Theorem 4.5.1], [Scharlemann1977].
The case 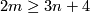 is called a `metastable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there are analogous results with
is called a `metastable range' (for the classification problem; for the existence problem there are analogous results with 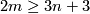 [Skopenkov2006,
[Skopenkov2006,  2,
2,  5]).
5]).
Knots in codimension 2 and the Haefliger trefoil knot [Skopenkov2016t, Example 2.1] show that the dimension restrictions are sharp (even for 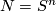 ) in the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
) in the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
Theorems 2.2 and 2.3 may be generalized as follows.
The Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4.
For every 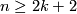 ,
, 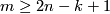 and closed
and closed  -connected
-connected  -manifold
-manifold  , any two embeddings of
, any two embeddings of  into
into  are isotopic.
are isotopic.
This was proved in [Penrose&Whitehead&Zeeman1961], [Haefliger1961], [Zeeman1962], [Irwin1965], [Hudson1969]. The proofs in [Haefliger&Hirsch1963], [Vrabec1977], [Weber1967], [Adachi1993,  7] work for homologically
7] work for homologically  -connected manifolds (see
-connected manifolds (see  3 for the definition; the proofs are non-trivial but the generalization is trivial, basically because the
3 for the definition; the proofs are non-trivial but the generalization is trivial, basically because the  -connectedness was used to ensure high enough connectedness of the complement in
-connectedness was used to ensure high enough connectedness of the complement in  to the image of
to the image of  , by Alexander duality and simple connectedness of the complement, so homological
, by Alexander duality and simple connectedness of the complement, so homological  -connectedness is sufficient).
-connectedness is sufficient).
Given Theorem 2.4 above, the case 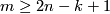 can be called a `stable range for
can be called a `stable range for  -connected manifolds'.
-connected manifolds'.
Note that if 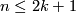 , then every closed
, then every closed  -connected
-connected  -manifold is a sphere, so the analogue of the Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4 in the smooth category is wrong, and in the PL category gives nothing more than the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
-manifold is a sphere, so the analogue of the Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4 in the smooth category is wrong, and in the PL category gives nothing more than the Unknotting Spheres Theorem 2.3.
For generalizations of the Haefliger-Zeeman Unknotting Theorem 2.4 see [Skopenkov2016e,  5] or [Hudson1967], [Hacon1968], [Hudson1972], [Gordon1972], [Kearton1979]. See also Theorem 6.1.
5] or [Hudson1967], [Hacon1968], [Hudson1972], [Gordon1972], [Kearton1979]. See also Theorem 6.1.
3 Notation and conventions
The following notations and conventions will be used below in this page and also in some other pages about embeddings, including those listed in Remark 1.4.
For a manifold  let
let 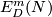 or
or 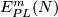 denote the set of
smooth or piecewise-linear (PL) embeddings
denote the set of
smooth or piecewise-linear (PL) embeddings 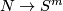 up to smooth or PL isotopy.
If the category is omitted, then the result holds (or a definition or a construction is given) in both categories.
up to smooth or PL isotopy.
If the category is omitted, then the result holds (or a definition or a construction is given) in both categories.
The sources of all embeddings are assumed to be compact.
Let 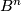 be a closed
be a closed  -ball in a closed connected
-ball in a closed connected  -manifold
-manifold  . Denote
. Denote 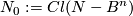 .
.
Let 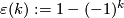 be
be  for
for  even and
even and 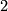 for
for  odd, so that
odd, so that 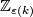 is
is 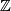 for
for  even and
even and 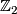 for
for  odd.
odd.
Denote by 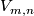 the Stiefel manifold of orthonormal
the Stiefel manifold of orthonormal  -frames in
-frames in  .
.
We omit 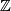 -coefficients from the notation of (co)homology groups.
-coefficients from the notation of (co)homology groups.
For a manifold 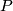 with boundary
with boundary 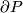 denote
denote 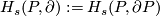 .
.
A closed manifold  is called homologically
is called homologically  -connected, if
-connected, if  is connected and
is connected and 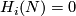 for every
for every  .
This condition is equivalent to
.
This condition is equivalent to  for each
for each 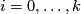 , where
, where 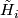 are reduced homology groups.
A pair
are reduced homology groups.
A pair 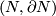 is called homologically
is called homologically  -connected, if
-connected, if 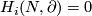 for every
for every 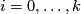 .
.
The self-intersection set of a map 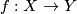 is
is 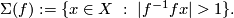
For a smooth embedding  denote by
denote by
-
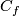 the closure of the complement in
the closure of the complement in 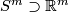 to a tight enough tubular neighborhood of
to a tight enough tubular neighborhood of 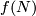 and
and
-
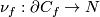 the restriction of the linear normal bundle of
the restriction of the linear normal bundle of 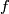 to the subspace of unit length vectors identified with
to the subspace of unit length vectors identified with 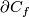 .
.
-
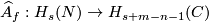 and
and 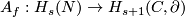 the homological Alexander duality isomorphisms, see the well-known Alexander Duality Lemmas of [Skopenkov2008], [Skopenkov2005].
the homological Alexander duality isomorphisms, see the well-known Alexander Duality Lemmas of [Skopenkov2008], [Skopenkov2005].
4 Embedded connected sum
Suppose that 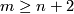 ,
,  is a closed connected
is a closed connected  -manifold and, if
-manifold and, if  is orientable, an orientation of
is orientable, an orientation of  is chosen.
Let us define the embedded connected sum operation
is chosen.
Let us define the embedded connected sum operation  of
of 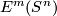 on
on 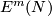 .
.
Represent isotopy classes ![[f]\in E^m(N)](/images/math/2/f/5/2f52f1701a659817e8b3dfbab85d0fef.png) and
and ![[g]\in E^m(S^n)](/images/math/0/0/3/003b3d9600f355a6b75926b59ee4b4c6.png) by embeddings
by embeddings 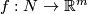 and
and 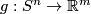 whose images are contained in disjoint balls.
Join the images of
whose images are contained in disjoint balls.
Join the images of  by an arc whose interior misses the images.
Let
by an arc whose interior misses the images.
Let ![[f]\#[g]](/images/math/b/5/0/b50485694938d441de43bc8d0d73e64c.png) be the isotopy class of the embedded connected sum of
be the isotopy class of the embedded connected sum of  and
and 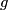 along this arc (compatible with the orientation, if
along this arc (compatible with the orientation, if  is orientable), cf. [Haefliger1966, Theorem 1.7], [Avvakumov2016,
is orientable), cf. [Haefliger1966, Theorem 1.7], [Avvakumov2016,  1].
1].
This operation is well-defined,
i.e. the isotopy class of class of the embedded connected sum depends only on the the isotopy classes ![[f]](/images/math/d/d/4/dd43b82529dd8d403c1585c5d151a163.png) and
and ![[g]](/images/math/0/8/a/08a05aeade465b1c6abe241850947aab.png) , and is independent of the choice of the path and of the representatives
, and is independent of the choice of the path and of the representatives 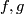 .
The proof of this fact is based on the construction of embedded connected sum of isotopies.
Although this fact is presumably classical, a proof was not written, cf. [Skopenkov2015a, Remark 2.3.a].
The proof is written for
.
The proof of this fact is based on the construction of embedded connected sum of isotopies.
Although this fact is presumably classical, a proof was not written, cf. [Skopenkov2015a, Remark 2.3.a].
The proof is written for 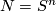 in [Skopenkov2015a,
in [Skopenkov2015a,  3, proof of the Standardization Lemma 2.1.b and beginning of proof of the Group structure Lemma 2.2 for
3, proof of the Standardization Lemma 2.1.b and beginning of proof of the Group structure Lemma 2.2 for 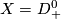 a point].
The proof for arbitrary closed connected
a point].
The proof for arbitrary closed connected  -manifold
-manifold  is analogous.
is analogous.
Moreover, for 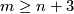 embedded connected sum defines a group structure on
embedded connected sum defines a group structure on 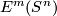 [Haefliger1966], and an action
[Haefliger1966], and an action  of
of 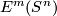 on
on 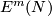 .
.
5 Some remarks on codimension 2 embeddings
The case of embeddings of 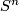 into
into 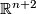 is the most extensively studied case of the Knotting Problem.
In this case there is an overwhelming multitude of isotopy classes of embeddings.
We present some speculations as to why the classification in codimension 2 should not be accessible for manifolds, not only for spheres.
is the most extensively studied case of the Knotting Problem.
In this case there is an overwhelming multitude of isotopy classes of embeddings.
We present some speculations as to why the classification in codimension 2 should not be accessible for manifolds, not only for spheres.
Let  be a closed connected
be a closed connected  -manifold.
Using embedded connected sum (
-manifold.
Using embedded connected sum ( 4) we can apparently produce an overwhelming multitude of embeddings
4) we can apparently produce an overwhelming multitude of embeddings 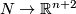 from the overwhelming multitude of embeddings
from the overwhelming multitude of embeddings 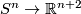 .
(However, note that for
.
(However, note that for 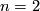 there are embeddings
there are embeddings 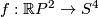 and
and 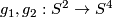 such that
such that 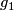 is not isotopic to
is not isotopic to 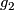 but
but 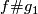 is isotopic to
is isotopic to 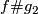 [Viro1973].)
One can also apply Artin's spinning construction [Artin1928]
[Viro1973].)
One can also apply Artin's spinning construction [Artin1928] 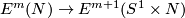 for
for 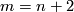 .
Thus the description of
.
Thus the description of 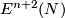 is a very hard open problem.
It would be interesting to give a more formal (e.g. algorithmic)
illustration of the hardness of this problem.
is a very hard open problem.
It would be interesting to give a more formal (e.g. algorithmic)
illustration of the hardness of this problem.
For studies of codimension 2 embeddings of manifolds up to the weaker relation of concordance see e.g. [Cappell&Shaneson1974].
6 Codimension 1 embeddings
Theorem 6.1.
(a) Any two smooth embeddings of 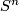 into
into 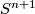 are smoothly isotopic for every
are smoothly isotopic for every 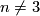 [Smale1961], [Smale1962a], [Barden1965].
[Smale1961], [Smale1962a], [Barden1965].
(b) Any two smooth embeddings of 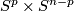 into
into 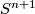 are smoothly isotopic for every
are smoothly isotopic for every 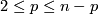 [Kosinski1961], [Wall1965], [Lucas&Neto&Saeki1996], cf. [Goldstein1967].
[Kosinski1961], [Wall1965], [Lucas&Neto&Saeki1996], cf. [Goldstein1967].
The analogue of part (a) holds
- for
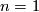 in the PL or topological category (Schöenfliess Theorem, 1912) [Rushing1973,
in the PL or topological category (Schöenfliess Theorem, 1912) [Rushing1973,  1.8].
1.8].
- for
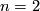 in the PL category (Alexander Theorem, 1923) [Rushing1973,
in the PL category (Alexander Theorem, 1923) [Rushing1973,  1.8].
1.8].
- for every
 in the topological locally flat category (Brown-Mazur-Moise Theorem, 1960) [Rushing1973, Generalized Schöenfliess Theorem 1.8.2].
in the topological locally flat category (Brown-Mazur-Moise Theorem, 1960) [Rushing1973, Generalized Schöenfliess Theorem 1.8.2].
The famous counterexample to the analogue of part (a) for 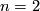 in the topological category is the Alexander horned sphere, see the corresponding Wikipedia article. The well-known very hard Schöenfliess Problem asks if each two PL embeddings of
in the topological category is the Alexander horned sphere, see the corresponding Wikipedia article. The well-known very hard Schöenfliess Problem asks if each two PL embeddings of 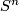 into
into 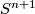 are isotopic for every
are isotopic for every 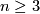 (this is equivalent to the description of
(this is equivalent to the description of 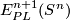 ).
).
Every embedding 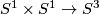 extends to an embedding either
extends to an embedding either 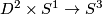 or
or 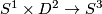 [Alexander1924]. Clearly, only the standard embedding extends to both.
[Alexander1924]. Clearly, only the standard embedding extends to both.
If it could be proven that this extension respects isotopy, this would give a 1-1 correspondence between 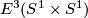 and the union of
and the union of 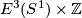 and
and 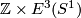 with `base points'
with `base points' 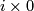 and
and 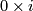 identified (where
identified (where 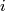 is the isotopy class of the standard inclusion
is the isotopy class of the standard inclusion 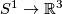 ). So the description of
). So the description of 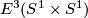 would be as hopeless as that of
would be as hopeless as that of 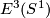 . Thus the description of
. Thus the description of 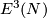 for
for  a sphere with handles is apparently hopeless.
a sphere with handles is apparently hopeless.
For more on higher-dimensional codimension 1 embeddings see e.g. [Lucas&Saeki2002].
7 References
- [Adachi1993] M. Adachi, Embeddings and immersions, Translated from the Japanese by Kiki Hudson. Translations of Mathematical Monographs, 124. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society (AMS), 1993. MR1225100 (95a:57039) Zbl 0810.57001
- [Alexander1924] J. W. Alexander, On the subdivision of 3-space by polyhedron, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 10, (1924) 6–8. Zbl 50.0659.01
- [Artin1928] E. Artin, Zur Isotopie zwei-dimensionaler Flaechen im
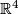 , Abh. Math. Sem. Hamburg Univ. 4 (1928) 174–177.
, Abh. Math. Sem. Hamburg Univ. 4 (1928) 174–177.
- [Avvakumov2016] S. Avvakumov, The classification of certain linked 3-manifolds in 6-space, Moscow Mathematical Journal, 16:1 (2016) 1-25. http://arxiv.org/abs/1408.3918.
- [Barden1965] D. Barden, Simply connected five-manifolds, Ann. of Math. (2) 82 (1965), 365–385. MR0184241 (32 #1714) Zbl 0136.20602
- [Cappell&Shaneson1974] S. E. Cappell and J. L. Shaneson, The codimension two placement problem and homology equivalent manifolds, Ann. of Math. (2) 99 (1974), 277–348. MR0339216 (49 #3978) Zbl 0279.57011
- [Gluck1963] H. Gluck, Unknotting
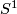 in
in 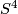 ., Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 69 (1963), 91-94. MR0142114 (25 #5507) Zbl 0108.36503
., Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 69 (1963), 91-94. MR0142114 (25 #5507) Zbl 0108.36503
- [Goldstein1967] R. Z. Goldstein, Piecewise linear unknotting of
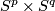 in
in 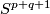 , Michigan Math. J. 14 (1967), 405–415. MR0220299 (36 #3365) Zbl 0157.54801
, Michigan Math. J. 14 (1967), 405–415. MR0220299 (36 #3365) Zbl 0157.54801
- [Goodwillie&Weiss1999] T. Goodwillie and M. Weiss, Embeddings from the point of view of immersion theory, II, Geometry and Topology, 3 (1999), 103-118. MR1694812 (2000c:57055a) Zbl 0927.57028
- [Gordon1972] C. Gordon, Embedding piecewise linear manifolds with boundary., Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 72 (1972), 21-25. MR0295359 (45 #4425) Zbl 0236.57009
- [Graham&Knuth&Patashnik89] R. Graham, D. Knuth, and O. Patashnik, Concrete Mathematics: A Foundation for Computer Science, Addison–Wesley, first published in 1989, ISBN 0-201-55802-5, https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r97002/temp/Concrete%20Mathematics%202e.pdf.
- [Hacon1968] D. Hacon, Embeddings of
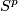 in
in 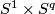 in the metastable range., Topology 7 (1968), 1-10. MR0222903 (36 #5953) Zbl 0153.53902
in the metastable range., Topology 7 (1968), 1-10. MR0222903 (36 #5953) Zbl 0153.53902
- [Haefliger&Hirsch1963] A. Haefliger and M. W. Hirsch, On the existence and classification of differentiable embeddings, Topology 2 (1963), 129–135. see also MR0149494 (26 #6981) Zbl 0113.38607
- [Haefliger1961] A. Haefliger, Plongements différentiables de variétés dans variétés., Comment. Math. Helv.36 (1961), 47-82. MR0145538 (26 #3069) Zbl 0102.38603
- [Haefliger1966] A. Haefliger, Differential embeddings of
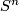 in
in 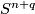 for
for 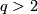 , Ann. of Math. (2) 83 (1966), 402–436. MR0202151 (34 #2024) Zbl 0151.32502
, Ann. of Math. (2) 83 (1966), 402–436. MR0202151 (34 #2024) Zbl 0151.32502
- [Hirsch1976] M. W. Hirsch, Differential topology., Graduate Texts in Mathematics, No. 33. Springer-Verlag., New York-Heidelberg, 1976. MR0448362 (56 #6669) Zbl 0356.57001
- [Hudson1967] J. Hudson, Piecewise linear embeddings, Ann. of Math. (2) 85 (1967) 1–31. MR0215308 (35 #6149) Zbl 0153.25601
- [Hudson1969] J. F. P. Hudson, Piecewise linear topology, W. A. Benjamin, Inc., New York-Amsterdam, 1969. MR0248844 (40 #2094) Zbl 0189.54507
- [Hudson1972] J. Hudson, Embeddings of bounded manifolds., Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 72 (1972), 11-20. MR0298679 (45 #7728) Zbl 0241.57006
- [Irwin1965] M. Irwin, Embeddings of polyhedral manifolds, Ann. of Math. (2) 82 (1965) 1–14. MR0182978 (32 #460) Zbl 0132.20003
- [Kearton1979] C. Kearton, Obstructions to embedding and isotopy in the metastable range, Math. Ann. 243 (1979), 103-113. MR0543720 (82k:57012) Zbl 0401.57033
- [Kosinski1961] A. Kosinski, On Alexander's theorem and knotted tori, In: Topology of 3-Manifolds, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, Ed. M.~K.~Fort, N.J., 1962, 55--57. Cf. Fort1962.
- [Lucas&Neto&Saeki1996] L. A. Lucas, O. M. Neto and O. Saeki, A generalization of Alexander's torus theorem to higher dimensions and an unknotting theorem for
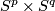 embedded in
embedded in  , Kobe J. Math. 13 (1996), no.2, 145–165. MR1442202 (98e:57041) Zbl 876.57045
, Kobe J. Math. 13 (1996), no.2, 145–165. MR1442202 (98e:57041) Zbl 876.57045
- [Lucas&Saeki2002] L. A. Lucas and O. Saeki, Embeddings of
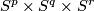 in
in 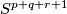 , Pacific J. Math. 207 (2002), no.2, 447–462. MR1972255 (2004c:57045) Zbl 1058.57022
, Pacific J. Math. 207 (2002), no.2, 447–462. MR1972255 (2004c:57045) Zbl 1058.57022
- [Penrose&Whitehead&Zeeman1961] R. Penrose, J. Whitehead and E. Zeeman, Imbedding of manifolds in Euclidean space., Ann. of Math. 73 (1961) 613–623. MR0124909 (23 #A2218) Zbl 0113.38101
- [Rourke&Sanderson1972] C. Rourke and B. Sanderson, Introduction to piecewise-linear topology., Ergebnisse der Mathematik und ihrer Grenzgebiete. Band 69. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer-Verlag. VIII, 1972. MR0665919 (83g:57009) Zbl 0254.57010
- [Rushing1973] T. Rushing, Topological embeddings., Pure and Applied Mathematics, 52. New York-London: Academic Press. XIII, 1973. MRMR0348752 (50 #1247) Zbl 0295.57003
- [Scharlemann1977] M. Scharlemann, Isotopy and cobordism of homology spheres in spheres., J. Lond. Math. Soc., II. Ser. 16 (1977), 559-567. MRMR0464246 (57 #4180) Zbl 0375.57003
- [Skopenkov2005] A. Skopenkov, A classification of smooth embeddings of 4-manifolds in 7-space, Topol. Appl., 157 (2010) 2094-2110. Available at the arXiv:0512594.
- [Skopenkov2006] A. Skopenkov, Embedding and knotting of manifolds in Euclidean spaces, in: Surveys in Contemporary Mathematics, Ed. N. Young and Y. Choi, London Math. Soc. Lect. Notes, 347 (2008) 248-342. Available at the arXiv:0604045.
- [Skopenkov2008] A. Skopenkov, A classification of smooth embeddings of 3-manifolds in 6-space, Math. Z. 260 (2008), no.3, 647–672. Available at the arXiv:0603429MR2434474 (2010e:57028) Zbl 1167.57013
- [Skopenkov2015a] A. Skopenkov, A classification of knotted tori, Proc. A of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 150:2 (2020), 549-567. Full version: http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.04470
- [Skopenkov2016e] A. Skopenkov, Embeddings just below the stable range: classification, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016f] A. Skopenkov, 4-manifolds in 7-space, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016h] A. Skopenkov, High codimension links, to appear in Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016i] A. Skopenkov, Isotopy, submitted to Bull. Man. Atl.
- [Skopenkov2016k] A. Skopenkov, Knotted tori, preprint.
- [Skopenkov2016t] A. Skopenkov, 3-manifolds in 6-space, to appear in Boll. Man. Atl.
- [Smale1961] S. Smale, Generalized Poincaré's conjecture in dimensions greater than four, Ann. of Math. (2) 74 (1961), 391–406. MR0137124 (25 #580) Zbl 0099.39202
- [Smale1962a] S. Smale, On the structure of manifolds, Amer. J. Math. 84 (1962), 387–399. MR0153022 (27 #2991) Zbl 0109.41103
- [Stallings1963] J. Stallings, On topologically unknotted spheres., (1963). MRMR0149458 (26 #6946) Zbl 0121.18202
- [Viro1973] O. J. Viro, Local knotting of sub-manifolds, Mat. Sb. (N.S.) 90(132) (1973), 173–183, 325. MR0370606 (51 #6833)
- [Vrabec1977] J. Vrabec, Knotting a
 -connected closed
-connected closed 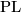
 -manifold in
-manifold in 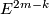 , Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 233 (1977), 137–165. MR0645405 (58 #31097) Zbl 386.57013
, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 233 (1977), 137–165. MR0645405 (58 #31097) Zbl 386.57013
- [Wall1965] C. T. C. Wall, Unknotting tori in codimension one and spheres in codimension two., Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 61 (1965), 659-664. MR0184249 (32 #1722) Zbl 0135.41602
- [Wall1999] C. T. C. Wall, Surgery on compact manifolds, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 1999. MR1687388 (2000a:57089) Zbl 0935.57003
- [Weber1967] C. Weber, Plongements de polyedres dans le domaine metastable, Comment. Math. Helv. 42 (1967), 1-27. MR0238330 (38 #6606) Zbl 0152.22402
- [Weiss] M. Weiss, private communication
- [Weiss96] M. Weiss, Calculus of Embeddings, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 33 (1996), 177-187.
- [Wu1958] W. Wu, On the realization of complexes in euclidean spaces. I, Sci. Sinica 7 (1958), 251–297. MR0099026 (20 #5471) Zbl 0183.28302
- [Wu1958a] W. Wu, On the realization of complexes in euclidean spaces. II, Sci. Sinica 7 (1958), 365–387.
- [Wu1959] W. Wu, On the realization of complexes in euclidean spaces. III, Sci. Sinica 8 (1959), 133–150. MR0098365 (20 #4825b) Zbl 0207.53104
- [Zeeman1960] E. Zeeman, Unknotting spheres in five dimensions, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 66 (1960) 198. MR0117737 (22 #8512a) Zbl 0117.40904
- [Zeeman1962] E. C. Zeeman, Isotopies and knots in manifolds, Topology of 3-manifolds and related topics (Proc. The Univ. of Georgia Institute, 1961), Prentice-Hall (1962), 187–193. MR0140097 (25 #3520) Zbl 1246.57069
- [Zeeman1993] E.C. Zeeman, A Brief History of Topology, UC Berkeley, October 27, 1993, On the occasion of Moe Hirsch's 60th birthday, http://zakuski.utsa.edu/~gokhman/ecz/hirsch60.pdf
 such that given space admits an embedding into
such that given space admits an embedding into  -dimensional Euclidean space
-dimensional Euclidean space  .
.
The Embedding and Knotting Problems have played an outstanding role in the development of topology. Various methods for the investigation of these problems were created by such classical figures as G. Alexander, H. Hopf, E. van Kampen, K. Kuratowski, S. MacLane, L. S. Pontryagin, R. Thom, H. Whitney, M. Atiyah, F. Hirzebruch, R. Penrose, J. H. C. Whitehead, C. Zeeman, W. Browder, J. Levine, S. P. Novikov, A. Haefliger, M. Hirsch, J. F. P. Hudson, M. Irwin and others.
The Knotting Problem is related to other branches of mathematics, most importantly, to algebraic topology (see Remark 1.4 below). See also Wikipedia article on knot theory and [Skopenkov2016t, Example 2.3].