Blanchfield form
Markpowell13 (Talk | contribs) |
(→Introduction) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| − | After Poincar\'{e} and Lefschetz, a closed manifold $N^{n}$ has a bilinear intersection form defined on its homology: | + | After Poincar\'{e} and Lefschetz, a closed oriented manifold $N^{n}$ has a bilinear intersection form defined on its homology: |
| − | $$ | + | $$I_N \colon H_k(N;\mathbb{Z}) \times H_{n-k}(N;\mathbb{Z}) \to \mathbb{Z}; ([p],[q]) \mapsto \langle p, q \rangle$$ |
| + | such that | ||
| + | $$I_N(x,y) = (-)^{k(n-k)}I_N(y,x).$$ | ||
Given a ${k}$--chain $p \in C_{k}(N;\mathbb{Z})$ and an $(n-k)$--chain $q \in C_{n-k}(N;\mathbb{Z})$ which is transverse to $q$, the signed count of the intersections between $p$ and $q$ gives an intersection number $\langle\, p \, , \, q\, \rangle \in \mathbb{Z}$. | Given a ${k}$--chain $p \in C_{k}(N;\mathbb{Z})$ and an $(n-k)$--chain $q \in C_{n-k}(N;\mathbb{Z})$ which is transverse to $q$, the signed count of the intersections between $p$ and $q$ gives an intersection number $\langle\, p \, , \, q\, \rangle \in \mathbb{Z}$. | ||
By bilinearity, the intersection form vanishes on the torsion part of the homology. The analogue of the intersection pairing for the torsion part of the homology of a closed manifold $N^n$ is the bilinear $\Q/\mathbb{Z}$--valued linking form, which is due to Seifert: | By bilinearity, the intersection form vanishes on the torsion part of the homology. The analogue of the intersection pairing for the torsion part of the homology of a closed manifold $N^n$ is the bilinear $\Q/\mathbb{Z}$--valued linking form, which is due to Seifert: | ||
| − | $$L_N \colon TH_{\ell}(N;\mathbb{Z}) \times TH_{n-\ell-1}(N;\mathbb{Z}) \to \Q/\mathbb{Z}.$$ | + | $$L_N \colon TH_{\ell}(N;\mathbb{Z}) \times TH_{n-\ell-1}(N;\mathbb{Z}) \to \Q/\mathbb{Z}$$ |
| + | such that | ||
| + | $$L_N(x,y) = (-)^{\ell(n-\ell-1)}L_N(y,x).$$ | ||
Revision as of 17:23, 6 January 2013
|
This page has not been refereed. The information given here might be incomplete or provisional. |
1 Introduction
After Poincar\'{e} and Lefschetz, a closed oriented manifold 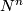 has a bilinear intersection form defined on its homology:
has a bilinear intersection form defined on its homology:
![\displaystyle I_N \colon H_k(N;\mathbb{Z}) \times H_{n-k}(N;\mathbb{Z}) \to \mathbb{Z}; ([p],[q]) \mapsto \langle p, q \rangle](/images/math/e/b/d/ebddd6200fa14a95e472da816b20076d.png)
such that
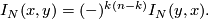
Given a 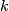 --chain
--chain 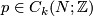 and an
and an 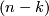 --chain
--chain 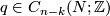 which is transverse to
which is transverse to 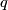 , the signed count of the intersections between
, the signed count of the intersections between 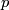 and
and 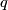 gives an intersection number
gives an intersection number 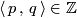 .
.
By bilinearity, the intersection form vanishes on the torsion part of the homology. The analogue of the intersection pairing for the torsion part of the homology of a closed manifold 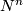 is the bilinear
is the bilinear 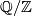 --valued linking form, which is due to Seifert:
--valued linking form, which is due to Seifert:
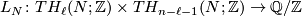
such that
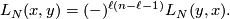
Given ![[x] \in TH_\ell(N;\mathbb{Z})](/images/math/d/a/4/da4b6d59ddf4a9b94a1b58801617ff44.png) and
and ![[y] \in TH_{n-\ell-1}(N;\mathbb{Z})](/images/math/d/c/f/dcf6aac3ea142090318edf382dd35df1.png) represented by cycles
represented by cycles 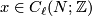 , let
, let 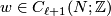 be such that
be such that 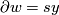 , for some
, for some 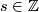 . Then we define:
. Then we define:
![\displaystyle L_N([x],[y]) := \langle x, w \rangle/s \in \Q/\mathbb{Z}.](/images/math/7/d/8/7d8a8698301793fadf55353b7d894a0e.png)
The resulting element is independent of the choices of 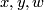 and
and  .
.
As an example, let 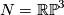 , so that
, so that 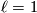 and
and 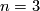 . Now
. Now 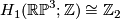 . Let
. Let 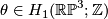 be the non--trivial element. To compute the linking
be the non--trivial element. To compute the linking 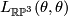 , consider
, consider 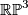 modelled as
modelled as 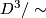 , with antipodal points on
, with antipodal points on 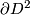 identified, and choose two representative
identified, and choose two representative 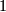 --chains
--chains  and
and 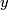 for
for 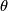 . Let
. Let  be the straight line between north and south poles and let
be the straight line between north and south poles and let 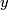 be half of the equator. Now
be half of the equator. Now 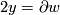 , where
, where 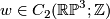 is the 2--disk whose boundary is the equator. We see that
is the 2--disk whose boundary is the equator. We see that 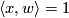 , so that
, so that
![\displaystyle L_{\mathbb{RP}^3}(\theta,\theta) = L_{\mathbb{RP}^3}([x],[y]) = \langle x,y \rangle/2 = 1/2.](/images/math/0/5/7/05725e0e70a522c8cbd35b7582e9aedd.png)
In 1939 Reidemeister [Reidemeister1939] defined an equivariant, sesquilinear intersection form on the homology of a covering space 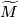 of an
of an  -dimensional closed manifold
-dimensional closed manifold 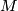 whose deck transformation group
whose deck transformation group 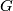 is abelian.
is abelian.
![\displaystyle \begin{array}{rcl} I_{\widetilde{M}} \colon H_k(\widetilde{M};\mathbb{Z}) \times H_{m-k}(\widetilde{M};\mathbb{Z}) &\to & \mathbb{Z}[G]; \\ ([p],[q]) & \mapsto & \sum_{g \in G} \langle g \cdot p, q \rangle g^{-1}. \end{array}](/images/math/b/b/a/bbac3363960fa95733978bfef7172f7f.png)
The intersections of each possible 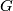 -translate of
-translate of 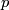 and
and 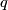 are counted, and indexed according to the deck transformation which produced that intersection number.
are counted, and indexed according to the deck transformation which produced that intersection number.
In his 1954 Princeton PhD thesis R.~C.~Blanchfield [Blanchfield1957] made the corresponding generalisation for linking forms. Let 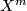 be a compact manifold, now possibly with non--empty boundary, with a surjective homomorphism
be a compact manifold, now possibly with non--empty boundary, with a surjective homomorphism 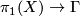 , for some free abelian group
, for some free abelian group 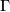 . Let
. Let ![\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/a/3/1/a3125186741639dcc06e77c618736635.png) be the group ring of
be the group ring of 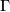 and let
and let 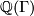 be its field of fractions.
be its field of fractions.
![\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/a/3/1/a3125186741639dcc06e77c618736635.png) -torsion submodule of a
-torsion submodule of a ![\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/a/3/1/a3125186741639dcc06e77c618736635.png) module
module 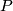 is the set
is the set ![\displaystyle TP:= \{p \in P \,|\, ap=0 \text{ for some } a \in \mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]\}.](/images/math/2/3/6/236be0676d35583ae0d92faf468aa3cc.png)
The Blanchfield form is a sesquilinear ![\Q(\Gamma)/\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/e/8/a/e8a5de95ce9c5d26baf5ef76ffeef634.png) --valued form which is defined on the
--valued form which is defined on the ![\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/a/3/1/a3125186741639dcc06e77c618736635.png) -torsion submodules of the homology of the
-torsion submodules of the homology of the 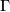 --cover
--cover 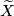 of
of 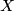 :
:
![\displaystyle \mathop{\mathrm{Bl}} \colon TH_\ell(\widetilde{X};\mathbb{Z}) \times TH_{m-\ell-1}(\widetilde{X},\partial\widetilde{X};\mathbb{Z}) \to \Q(\Gamma)/\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma].](/images/math/a/2/a/a2a6c80e045d59e7ecf06ace6e9ec15c.png)
![\displaystyle [x] \in TH_\ell(\widetilde{X};\mathbb{Z}) \cong TH_\ell(X;\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma])](/images/math/d/5/5/d55dd349382e40c3e000068222d15ffe.png)
![\displaystyle [y] \in TH_{m-\ell-1}(\widetilde{X},\partial \widetilde{X};\mathbb{Z}) \cong TH_{m-\ell-1}(X,\partial X;\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma])](/images/math/a/1/2/a1287db438b45a10e05cb69d69c33415.png)
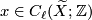 and
and 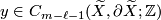 , let
, let 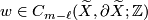 be such that
be such that 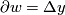 , for some
, for some ![\Delta \in \mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/0/3/a/03a07519b417c559188d4f50e3899ac2.png) . Then we define:
. Then we define:
![\displaystyle \mathop{\mathrm{Bl}}([x],[y]) := \sum_{g \in \Gamma} \langle g \cdot x, w \rangle g^{-1}/\Delta \in \Q(\Gamma)/\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma],](/images/math/4/d/5/4d53cdaa4a4f14099980fcb1e7472841.png)
where 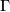 acts on
acts on 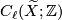 by the action induced from the deck transformation.
by the action induced from the deck transformation.
We now turn to an example. For simplicity we will focus on the case of knots in 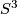 . For a knot
. For a knot 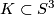 , let
, let 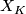 denote its exterior, which is the complement of a regular neighbourhood of
denote its exterior, which is the complement of a regular neighbourhood of 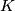 :
: 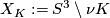 . Now
. Now 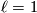 ,
, 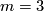 and the abelianisation gives a homomorphism
and the abelianisation gives a homomorphism 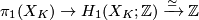 . The Blanchfield form can in this case be defined without relative homology, on
. The Blanchfield form can in this case be defined without relative homology, on ![H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \cong H_1(\widetilde{X}_K;\mathbb{Z})](/images/math/3/0/a/30a5f3c1b63fd8fb88f048752cb3b0ed.png) . The form
. The form
![\displaystyle \mathop{\mathrm{Bl}} \colon H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \times H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \to \Q(\mathbb{Z})/\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]](/images/math/e/3/d/e3dc73a0941f52f5f5c726b85b88a499.png)
is non--singular, sesquilinear and Hermitian. Note that ![H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}])](/images/math/4/6/b/46b729298a9b112e3dec6fe78d83b20c.png) is entirely
is entirely ![\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]](/images/math/1/4/5/145a993dc91cbaa4548057383bb478b1.png) --torsion, so
--torsion, so ![H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) = TH_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}])](/images/math/d/8/9/d89fcb6c4897f5d3d28aed868a29c8ea.png) . The adjoint of this form is given by the following sequence of homomorphisms:
. The adjoint of this form is given by the following sequence of homomorphisms:
![\displaystyle \begin{aligned} &H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H_1(X_K,\partial X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H^2(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \\ & \to H^1(X_K;\Q(\mathbb{Z})/\Q[\mathbb{Z}]) \to \Hom_{\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]}(H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]),\Q(\mathbb{Z})/\Q[\mathbb{Z}]), \end{aligned}](/images/math/9/9/8/998f85b04ad5784e012c8ff295b10f2a.png)
which arise from the long exact sequence of a pair, equivariant Poincar\'{e}--Lefschetz duality, a Bockstein homomorphism, and universal coefficients. Showing that these maps are isomorphisms proves that \mathop{\mathrm{Bl}}$ is non--singular. A good exercise is to trace through this sequence of isomorphisms to check that it really does coincide with the definition of the Blanchfield form given above.
One of the Blanchfield form's main applications is in knot concordance, a notion first defined in [Fox&Milnor1959]. Two knots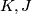 are concordant if there is an annulus embedded in
are concordant if there is an annulus embedded in 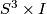 whose boundary is
whose boundary is 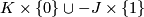 . A knot which is concordant to the unknot is called a slice knot; equivalently a slice knot bounds an embedded disk in
. A knot which is concordant to the unknot is called a slice knot; equivalently a slice knot bounds an embedded disk in 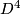 . We say that a Blanchfield form is metabolic if there is a submodule
. We say that a Blanchfield form is metabolic if there is a submodule ![P \subset H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}])](/images/math/9/3/8/938003a52a52d5c1016d2ad7d6deaa60.png) which is self--orthogonal with respect to
which is self--orthogonal with respect to 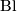 , called a metaboliser. The Blanchfield form of a slice knot is metabolic, so that the Blanchfield form provides an obstruction to concordance [Kearton], which is equivalent to Levine's Seifert form obstruction [Levine], but which is more intrinsic, since for a given knot there are many Seifert surfaces but only one knot exterior. The proof that Blanchfield form of a slice knot is metabolic rests on the observation that, if
, called a metaboliser. The Blanchfield form of a slice knot is metabolic, so that the Blanchfield form provides an obstruction to concordance [Kearton], which is equivalent to Levine's Seifert form obstruction [Levine], but which is more intrinsic, since for a given knot there are many Seifert surfaces but only one knot exterior. The proof that Blanchfield form of a slice knot is metabolic rests on the observation that, if 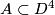 is a slice disk for
is a slice disk for 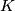 , the Blanchfield form vanishes on the kernel of the map
, the Blanchfield form vanishes on the kernel of the map ![\displaystyle H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H_1(D^4\setminus \nu A;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]).](/images/math/6/0/b/60b126ae6a3f36837e2e3b54015454e9.png)
For high--dimensional knots, 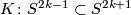 , where
, where 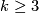 , the Blanchfield form is metabolic if and only if
, the Blanchfield form is metabolic if and only if 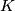 is slice [Levine, Kearton]. Levine [Levine2] classified the modules which can arise as the homology of high--dimensional knots: the key property that a knot module must satisfy is Blanchfield duality. For a comprehensive account of the algebraic theory of high--dimensional knots, such as how the Blanchfield form can be used to compute the high--dimensional knot cobordism group, see [RanickiHighDimKnotTheory].
is slice [Levine, Kearton]. Levine [Levine2] classified the modules which can arise as the homology of high--dimensional knots: the key property that a knot module must satisfy is Blanchfield duality. For a comprehensive account of the algebraic theory of high--dimensional knots, such as how the Blanchfield form can be used to compute the high--dimensional knot cobordism group, see [RanickiHighDimKnotTheory].
For classical knots in the 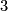 --sphere, there are many non--slice knots with metabolic Blanchfield form, the first of which were found in [CassonGordon]. Cochran, Orr and Teichner [COT] defined an infinite filtration of the knot concordance group, each of whose associated graded groups has infinite rank [COT2, Cochran&Teichner2007, Cochran&Harvey&Leidy2009]. Their obstructions are obtained by defining representations into progressively more solvable groups. The Blanchfield form, and so--called higher order Blanchfield forms, play a crucial r\^{o}le in controlling the representations which extend from the knot exterior across a potential slice disc exterior
--sphere, there are many non--slice knots with metabolic Blanchfield form, the first of which were found in [CassonGordon]. Cochran, Orr and Teichner [COT] defined an infinite filtration of the knot concordance group, each of whose associated graded groups has infinite rank [COT2, Cochran&Teichner2007, Cochran&Harvey&Leidy2009]. Their obstructions are obtained by defining representations into progressively more solvable groups. The Blanchfield form, and so--called higher order Blanchfield forms, play a crucial r\^{o}le in controlling the representations which extend from the knot exterior across a potential slice disc exterior 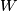 , whose existence one wishes to deny. Let
, whose existence one wishes to deny. Let 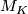 be the closed 3--manifold obtained from zero--framed surgery on
be the closed 3--manifold obtained from zero--framed surgery on 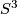 along
along 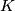 . Then the kernel
\[P:= \ker(H_1(M_K;\Q[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H_1(W;\Q[\mathbb{Z}]))\]
is a metaboliser for the rational Blanchfield form of
. Then the kernel
\[P:= \ker(H_1(M_K;\Q[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H_1(W;\Q[\mathbb{Z}]))\]
is a metaboliser for the rational Blanchfield form of 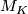 .
.
We give a special case of the results of [Cochran&Orr&Teichner2003] below, which shows the use of the Blanchfield form in an archetypal obstruction theorem for knot concordance problems. Given a closed 3--manifold 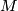 and a representation
and a representation 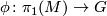 there is defined a real number
there is defined a real number 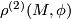 called the Cheeger--Gromov--Von--Neumann
called the Cheeger--Gromov--Von--Neumann 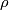 --invariant of
--invariant of 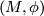 .
.
Theorem 1.1 Cochran-Orr-Teichner.
Let 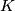 be a slice knot. Then there exists a metaboliser
be a slice knot. Then there exists a metaboliser 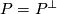 for the Blanchfield form of
for the Blanchfield form of 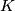 such that for each
such that for each 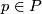 there is a representation
there is a representation 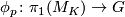 for which
for which 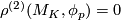 .
.
It is somewhat remarkable that the classical Blanchfield form continues to have new and interesting applications. For example, Borodzik and Friedl [BorodzikFriedl12I, BorodzikFriedl12II] recently used the minimal size of a matrix which represents the Blanchfield form of a given knot to compute many previously unknown unknotting numbers of low crossing number knots.
2 References
- [Blanchfield1957] R. C. Blanchfield, Intersection theory of manifolds with operators with applications to knot theory, Ann. of Math. (2) 65 (1957), 340–356. MR0085512 (19,53a) Zbl 0080.16601
- [BorodzikFriedl12I, BorodzikFriedl12II] Template:BorodzikFriedl12I, BorodzikFriedl12II
- [COT] Template:COT
- [COT2, Cochran&Teichner2007, Cochran&Harvey&Leidy2009] Template:COT2, Cochran&Teichner2007, Cochran&Harvey&Leidy2009
- [CassonGordon] Template:CassonGordon
- [Cochran&Orr&Teichner2003] T. D. Cochran, K. E. Orr and P. Teichner, Knot concordance, Whitney towers and
 -signatures, Ann. of Math. (2) 157 (2003), no.2, 433–519. MR1973052 (2004i:57003) Zbl 1044.57001
-signatures, Ann. of Math. (2) 157 (2003), no.2, 433–519. MR1973052 (2004i:57003) Zbl 1044.57001
- [Fox&Milnor1959] Template:Fox&Milnor1959
- [Kearton] Template:Kearton
- [Levine] Template:Levine
- [Levine, Kearton] Template:Levine, Kearton
- [Levine2] Template:Levine2
- [RanickiHighDimKnotTheory] Template:RanickiHighDimKnotTheory
- [Reidemeister1939] K. Reidemeister, Durchschnitt und Schnitt von Homotopieketten, Monatsh. Math. Phys. 48 (1939), 226–239. MR0000634 (1,105h) Zbl 0021.43104
![\displaystyle I_N \colon H_k(N;\mathbb{Z}) \times H_{n-k}(N;\mathbb{Z}) \to \mathbb{Z}; ([p],[q]) \mapsto \langle p, q \rangle](/images/math/e/b/d/ebddd6200fa14a95e472da816b20076d.png)
such that
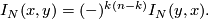
Given a 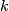 --chain
--chain 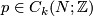 and an
and an 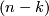 --chain
--chain 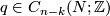 which is transverse to
which is transverse to 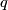 , the signed count of the intersections between
, the signed count of the intersections between 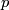 and
and 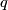 gives an intersection number
gives an intersection number 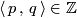 .
.
By bilinearity, the intersection form vanishes on the torsion part of the homology. The analogue of the intersection pairing for the torsion part of the homology of a closed manifold 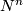 is the bilinear
is the bilinear 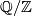 --valued linking form, which is due to Seifert:
--valued linking form, which is due to Seifert:
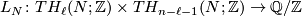
such that
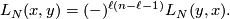
Given ![[x] \in TH_\ell(N;\mathbb{Z})](/images/math/d/a/4/da4b6d59ddf4a9b94a1b58801617ff44.png) and
and ![[y] \in TH_{n-\ell-1}(N;\mathbb{Z})](/images/math/d/c/f/dcf6aac3ea142090318edf382dd35df1.png) represented by cycles
represented by cycles 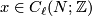 , let
, let 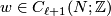 be such that
be such that 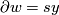 , for some
, for some 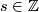 . Then we define:
. Then we define:
![\displaystyle L_N([x],[y]) := \langle x, w \rangle/s \in \Q/\mathbb{Z}.](/images/math/7/d/8/7d8a8698301793fadf55353b7d894a0e.png)
The resulting element is independent of the choices of 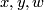 and
and  .
.
As an example, let 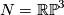 , so that
, so that 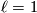 and
and 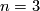 . Now
. Now 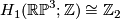 . Let
. Let 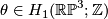 be the non--trivial element. To compute the linking
be the non--trivial element. To compute the linking 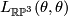 , consider
, consider 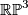 modelled as
modelled as 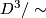 , with antipodal points on
, with antipodal points on 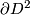 identified, and choose two representative
identified, and choose two representative 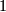 --chains
--chains  and
and 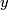 for
for 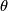 . Let
. Let  be the straight line between north and south poles and let
be the straight line between north and south poles and let 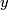 be half of the equator. Now
be half of the equator. Now 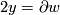 , where
, where 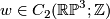 is the 2--disk whose boundary is the equator. We see that
is the 2--disk whose boundary is the equator. We see that 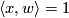 , so that
, so that
![\displaystyle L_{\mathbb{RP}^3}(\theta,\theta) = L_{\mathbb{RP}^3}([x],[y]) = \langle x,y \rangle/2 = 1/2.](/images/math/0/5/7/05725e0e70a522c8cbd35b7582e9aedd.png)
In 1939 Reidemeister [Reidemeister1939] defined an equivariant, sesquilinear intersection form on the homology of a covering space 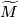 of an
of an  -dimensional closed manifold
-dimensional closed manifold 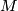 whose deck transformation group
whose deck transformation group 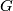 is abelian.
is abelian.
![\displaystyle \begin{array}{rcl} I_{\widetilde{M}} \colon H_k(\widetilde{M};\mathbb{Z}) \times H_{m-k}(\widetilde{M};\mathbb{Z}) &\to & \mathbb{Z}[G]; \\ ([p],[q]) & \mapsto & \sum_{g \in G} \langle g \cdot p, q \rangle g^{-1}. \end{array}](/images/math/b/b/a/bbac3363960fa95733978bfef7172f7f.png)
The intersections of each possible 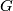 -translate of
-translate of 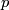 and
and 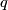 are counted, and indexed according to the deck transformation which produced that intersection number.
are counted, and indexed according to the deck transformation which produced that intersection number.
In his 1954 Princeton PhD thesis R.~C.~Blanchfield [Blanchfield1957] made the corresponding generalisation for linking forms. Let 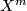 be a compact manifold, now possibly with non--empty boundary, with a surjective homomorphism
be a compact manifold, now possibly with non--empty boundary, with a surjective homomorphism 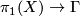 , for some free abelian group
, for some free abelian group 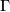 . Let
. Let ![\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/a/3/1/a3125186741639dcc06e77c618736635.png) be the group ring of
be the group ring of 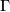 and let
and let 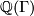 be its field of fractions.
be its field of fractions.
![\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/a/3/1/a3125186741639dcc06e77c618736635.png) -torsion submodule of a
-torsion submodule of a ![\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/a/3/1/a3125186741639dcc06e77c618736635.png) module
module 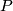 is the set
is the set ![\displaystyle TP:= \{p \in P \,|\, ap=0 \text{ for some } a \in \mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]\}.](/images/math/2/3/6/236be0676d35583ae0d92faf468aa3cc.png)
The Blanchfield form is a sesquilinear ![\Q(\Gamma)/\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/e/8/a/e8a5de95ce9c5d26baf5ef76ffeef634.png) --valued form which is defined on the
--valued form which is defined on the ![\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/a/3/1/a3125186741639dcc06e77c618736635.png) -torsion submodules of the homology of the
-torsion submodules of the homology of the 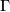 --cover
--cover 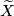 of
of 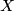 :
:
![\displaystyle \mathop{\mathrm{Bl}} \colon TH_\ell(\widetilde{X};\mathbb{Z}) \times TH_{m-\ell-1}(\widetilde{X},\partial\widetilde{X};\mathbb{Z}) \to \Q(\Gamma)/\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma].](/images/math/a/2/a/a2a6c80e045d59e7ecf06ace6e9ec15c.png)
![\displaystyle [x] \in TH_\ell(\widetilde{X};\mathbb{Z}) \cong TH_\ell(X;\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma])](/images/math/d/5/5/d55dd349382e40c3e000068222d15ffe.png)
![\displaystyle [y] \in TH_{m-\ell-1}(\widetilde{X},\partial \widetilde{X};\mathbb{Z}) \cong TH_{m-\ell-1}(X,\partial X;\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma])](/images/math/a/1/2/a1287db438b45a10e05cb69d69c33415.png)
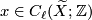 and
and 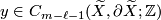 , let
, let 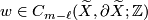 be such that
be such that 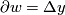 , for some
, for some ![\Delta \in \mathbb{Z}[\Gamma]](/images/math/0/3/a/03a07519b417c559188d4f50e3899ac2.png) . Then we define:
. Then we define:
![\displaystyle \mathop{\mathrm{Bl}}([x],[y]) := \sum_{g \in \Gamma} \langle g \cdot x, w \rangle g^{-1}/\Delta \in \Q(\Gamma)/\mathbb{Z}[\Gamma],](/images/math/4/d/5/4d53cdaa4a4f14099980fcb1e7472841.png)
where 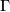 acts on
acts on 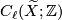 by the action induced from the deck transformation.
by the action induced from the deck transformation.
We now turn to an example. For simplicity we will focus on the case of knots in 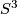 . For a knot
. For a knot 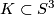 , let
, let 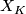 denote its exterior, which is the complement of a regular neighbourhood of
denote its exterior, which is the complement of a regular neighbourhood of 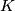 :
: 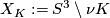 . Now
. Now 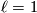 ,
, 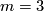 and the abelianisation gives a homomorphism
and the abelianisation gives a homomorphism 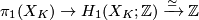 . The Blanchfield form can in this case be defined without relative homology, on
. The Blanchfield form can in this case be defined without relative homology, on ![H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \cong H_1(\widetilde{X}_K;\mathbb{Z})](/images/math/3/0/a/30a5f3c1b63fd8fb88f048752cb3b0ed.png) . The form
. The form
![\displaystyle \mathop{\mathrm{Bl}} \colon H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \times H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \to \Q(\mathbb{Z})/\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]](/images/math/e/3/d/e3dc73a0941f52f5f5c726b85b88a499.png)
is non--singular, sesquilinear and Hermitian. Note that ![H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}])](/images/math/4/6/b/46b729298a9b112e3dec6fe78d83b20c.png) is entirely
is entirely ![\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]](/images/math/1/4/5/145a993dc91cbaa4548057383bb478b1.png) --torsion, so
--torsion, so ![H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) = TH_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}])](/images/math/d/8/9/d89fcb6c4897f5d3d28aed868a29c8ea.png) . The adjoint of this form is given by the following sequence of homomorphisms:
. The adjoint of this form is given by the following sequence of homomorphisms:
![\displaystyle \begin{aligned} &H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H_1(X_K,\partial X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H^2(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \\ & \to H^1(X_K;\Q(\mathbb{Z})/\Q[\mathbb{Z}]) \to \Hom_{\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]}(H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]),\Q(\mathbb{Z})/\Q[\mathbb{Z}]), \end{aligned}](/images/math/9/9/8/998f85b04ad5784e012c8ff295b10f2a.png)
which arise from the long exact sequence of a pair, equivariant Poincar\'{e}--Lefschetz duality, a Bockstein homomorphism, and universal coefficients. Showing that these maps are isomorphisms proves that \mathop{\mathrm{Bl}}$ is non--singular. A good exercise is to trace through this sequence of isomorphisms to check that it really does coincide with the definition of the Blanchfield form given above.
One of the Blanchfield form's main applications is in knot concordance, a notion first defined in [Fox&Milnor1959]. Two knots are concordant if there is an annulus embedded in
are concordant if there is an annulus embedded in 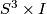 whose boundary is
whose boundary is 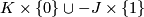 . A knot which is concordant to the unknot is called a slice knot; equivalently a slice knot bounds an embedded disk in
. A knot which is concordant to the unknot is called a slice knot; equivalently a slice knot bounds an embedded disk in 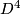 . We say that a Blanchfield form is metabolic if there is a submodule
. We say that a Blanchfield form is metabolic if there is a submodule ![P \subset H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}])](/images/math/9/3/8/938003a52a52d5c1016d2ad7d6deaa60.png) which is self--orthogonal with respect to
which is self--orthogonal with respect to 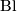 , called a metaboliser. The Blanchfield form of a slice knot is metabolic, so that the Blanchfield form provides an obstruction to concordance [Kearton], which is equivalent to Levine's Seifert form obstruction [Levine], but which is more intrinsic, since for a given knot there are many Seifert surfaces but only one knot exterior. The proof that Blanchfield form of a slice knot is metabolic rests on the observation that, if
, called a metaboliser. The Blanchfield form of a slice knot is metabolic, so that the Blanchfield form provides an obstruction to concordance [Kearton], which is equivalent to Levine's Seifert form obstruction [Levine], but which is more intrinsic, since for a given knot there are many Seifert surfaces but only one knot exterior. The proof that Blanchfield form of a slice knot is metabolic rests on the observation that, if 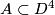 is a slice disk for
is a slice disk for 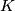 , the Blanchfield form vanishes on the kernel of the map
, the Blanchfield form vanishes on the kernel of the map ![\displaystyle H_1(X_K;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H_1(D^4\setminus \nu A;\mathbb{Z}[\mathbb{Z}]).](/images/math/6/0/b/60b126ae6a3f36837e2e3b54015454e9.png)
For high--dimensional knots, 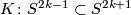 , where
, where 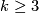 , the Blanchfield form is metabolic if and only if
, the Blanchfield form is metabolic if and only if 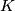 is slice [Levine, Kearton]. Levine [Levine2] classified the modules which can arise as the homology of high--dimensional knots: the key property that a knot module must satisfy is Blanchfield duality. For a comprehensive account of the algebraic theory of high--dimensional knots, such as how the Blanchfield form can be used to compute the high--dimensional knot cobordism group, see [RanickiHighDimKnotTheory].
is slice [Levine, Kearton]. Levine [Levine2] classified the modules which can arise as the homology of high--dimensional knots: the key property that a knot module must satisfy is Blanchfield duality. For a comprehensive account of the algebraic theory of high--dimensional knots, such as how the Blanchfield form can be used to compute the high--dimensional knot cobordism group, see [RanickiHighDimKnotTheory].
For classical knots in the 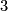 --sphere, there are many non--slice knots with metabolic Blanchfield form, the first of which were found in [CassonGordon]. Cochran, Orr and Teichner [COT] defined an infinite filtration of the knot concordance group, each of whose associated graded groups has infinite rank [COT2, Cochran&Teichner2007, Cochran&Harvey&Leidy2009]. Their obstructions are obtained by defining representations into progressively more solvable groups. The Blanchfield form, and so--called higher order Blanchfield forms, play a crucial r\^{o}le in controlling the representations which extend from the knot exterior across a potential slice disc exterior
--sphere, there are many non--slice knots with metabolic Blanchfield form, the first of which were found in [CassonGordon]. Cochran, Orr and Teichner [COT] defined an infinite filtration of the knot concordance group, each of whose associated graded groups has infinite rank [COT2, Cochran&Teichner2007, Cochran&Harvey&Leidy2009]. Their obstructions are obtained by defining representations into progressively more solvable groups. The Blanchfield form, and so--called higher order Blanchfield forms, play a crucial r\^{o}le in controlling the representations which extend from the knot exterior across a potential slice disc exterior 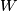 , whose existence one wishes to deny. Let
, whose existence one wishes to deny. Let 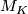 be the closed 3--manifold obtained from zero--framed surgery on
be the closed 3--manifold obtained from zero--framed surgery on 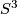 along
along 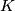 . Then the kernel
\[P:= \ker(H_1(M_K;\Q[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H_1(W;\Q[\mathbb{Z}]))\]
is a metaboliser for the rational Blanchfield form of
. Then the kernel
\[P:= \ker(H_1(M_K;\Q[\mathbb{Z}]) \to H_1(W;\Q[\mathbb{Z}]))\]
is a metaboliser for the rational Blanchfield form of 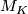 .
.
We give a special case of the results of [Cochran&Orr&Teichner2003] below, which shows the use of the Blanchfield form in an archetypal obstruction theorem for knot concordance problems. Given a closed 3--manifold 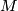 and a representation
and a representation 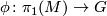 there is defined a real number
there is defined a real number 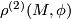 called the Cheeger--Gromov--Von--Neumann
called the Cheeger--Gromov--Von--Neumann 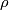 --invariant of
--invariant of 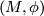 .
.
Theorem 1.1 Cochran-Orr-Teichner.
Let 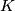 be a slice knot. Then there exists a metaboliser
be a slice knot. Then there exists a metaboliser 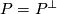 for the Blanchfield form of
for the Blanchfield form of 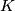 such that for each
such that for each 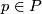 there is a representation
there is a representation 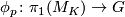 for which
for which 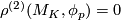 .
.
It is somewhat remarkable that the classical Blanchfield form continues to have new and interesting applications. For example, Borodzik and Friedl [BorodzikFriedl12I, BorodzikFriedl12II] recently used the minimal size of a matrix which represents the Blanchfield form of a given knot to compute many previously unknown unknotting numbers of low crossing number knots.
2 References
- [Blanchfield1957] R. C. Blanchfield, Intersection theory of manifolds with operators with applications to knot theory, Ann. of Math. (2) 65 (1957), 340–356. MR0085512 (19,53a) Zbl 0080.16601
- [BorodzikFriedl12I, BorodzikFriedl12II] Template:BorodzikFriedl12I, BorodzikFriedl12II
- [COT] Template:COT
- [COT2, Cochran&Teichner2007, Cochran&Harvey&Leidy2009] Template:COT2, Cochran&Teichner2007, Cochran&Harvey&Leidy2009
- [CassonGordon] Template:CassonGordon
- [Cochran&Orr&Teichner2003] T. D. Cochran, K. E. Orr and P. Teichner, Knot concordance, Whitney towers and
 -signatures, Ann. of Math. (2) 157 (2003), no.2, 433–519. MR1973052 (2004i:57003) Zbl 1044.57001
-signatures, Ann. of Math. (2) 157 (2003), no.2, 433–519. MR1973052 (2004i:57003) Zbl 1044.57001
- [Fox&Milnor1959] Template:Fox&Milnor1959
- [Kearton] Template:Kearton
- [Levine] Template:Levine
- [Levine, Kearton] Template:Levine, Kearton
- [Levine2] Template:Levine2
- [RanickiHighDimKnotTheory] Template:RanickiHighDimKnotTheory
- [Reidemeister1939] K. Reidemeister, Durchschnitt und Schnitt von Homotopieketten, Monatsh. Math. Phys. 48 (1939), 226–239. MR0000634 (1,105h) Zbl 0021.43104